|
|
Climate change and global warming are pressing issues affecting the planet and its inhabitants. Understanding these concepts is crucial to address their causes and effects. Climate change refers to long-term shifts in weather patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and wind.
Global warming, on the other hand, specifically refers to the increase in the Earth’s average surface temperature. Both climate change and global warming result from various factors and have significant environmental impacts.
Understanding Climate Change and Global Warming: Causes, Effects, and Greenhouse Gases
Climate change and global warming are interconnected yet distinct concepts that have a profound impact on our planet. To grasp these phenomena fully, it’s crucial to comprehend their unique characteristics and the factors driving them.
Climate Change vs. Global Warming:
Climate change encompasses the long-term alteration of weather patterns, which includes shifts in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and more. It represents a comprehensive transformation in the Earth’s climate system over extended periods.
On the other hand, global warming is a specific aspect of climate change, focusing on the consistent increase in the Earth’s average surface temperature. It highlights the sustained rising trend that contributes to broader climate changes.
From this video you can see that the impacts of global warming extend far beyond the melting polar ice. They encompass a broader spectrum of consequences, including the potential to reshape our geographical maps and displace communities living in cities and tropical islands.
The Human Influence on Climate Change
In this chart, per capita greenhouse gas emissions show how much pollution an average person produces. Total annual emissions reveal the biggest polluters in the world. Sometimes, it’s related to how many people live there. China and India are in the top three polluters because they have lots of people.
The primary driver of climate change, including global warming, is the excessive release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases act like an insulating blanket around the Earth, trapping heat and causing temperature increases.
Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), are key culprits. For instance, the combustion of fossil fuels, like coal, oil, and natural gas, releases substantial amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Deforestation, industrial processes, and agricultural activities also contribute to methane emissions.
Consequences of Climate Change
- The ramifications of climate change are profound and wide-ranging. They include rising sea levels due to the thermal expansion of seawater and the melting of polar ice caps. For instance, the melting of the Greenland ice sheet contributes to rising sea levels, posing a threat to coastal communities.
- Climate change leads to more frequent and severe extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heatwaves. These events have devastating effects on human populations and natural ecosystems.
- Biodiversity loss is another concerning consequence. As climate change alters habitats and disrupts ecosystems, species struggle to adapt, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
If the global temperatures were to increase by three degrees Celsius above the levels that existed before the Industrial Revolution, the consequences would be nothing short of catastrophic. Such a drastic temperature rise could lead to severe and far-reaching impacts on our planet, including more frequent and intense heatwaves, rising sea levels that threaten coastal communities, disruptions in ecosystems and biodiversity, and increased vulnerability to extreme weather events, among other detrimental effects. It underscores the urgency of addressing climate change to prevent such dire outcomes.
Is it Possible to Reverse Climate Change? Exploring Solutions for a Sustainable Future
While the impacts of climate change are already evident, there is hope for slowing down and even reversing global warming through coordinated global efforts. Examining potential solutions is essential in addressing this critical issue and preserving the planet for future generations.
The Imperative of Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
To combat climate change, a fundamental step is the significant reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. This reduction can be achieved by transitioning to cleaner forms of energy production. For instance, renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power offer sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. These sources generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, providing a crucial solution to curbing emissions.
Harnessing the Power of Renewable Energy

Wind Power
Wind energy utilizes the natural force of the wind to generate electricity. This process doesn’t release greenhouse gases and has seen widespread adoption in many parts of the world, including countries like Denmark which have made substantial investments in wind energy. In 2022, Denmark’s wind energy production exceeded 19 terawatt-hours, thanks to improved technology that lowered costs. Over half of Denmark’s electricity comes from wind, with 6,296 turbines generating around seven gigawatts.
Solar Power
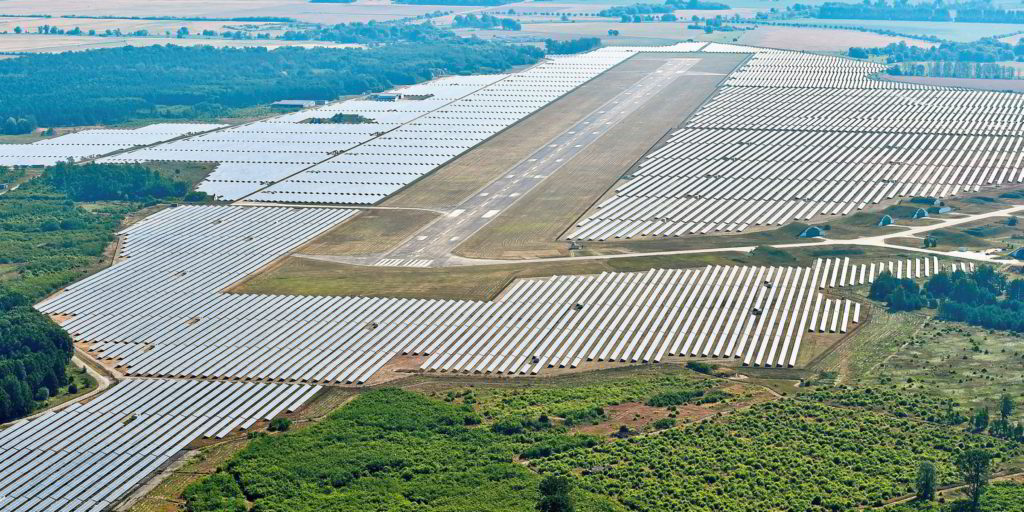

Solar energy converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. Countries like Germany and the United States have made significant strides in solar power adoption, contributing to reduced carbon emissions. Despite its limited sunshine, Germany has a high solar output and ongoing research, with the government’s goal of a fully renewable energy system by 2035 likely to boost the industry.
Hydroelectric Power
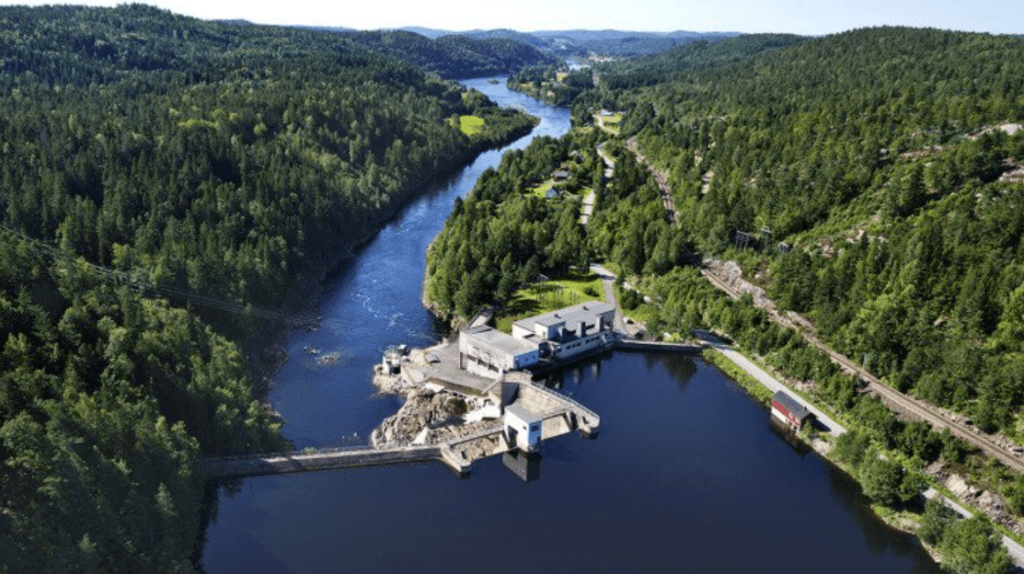

Hydroelectric power generates electricity from water flow, typically in dams or river systems. Nations like Norway and Canada have extensive hydroelectric power infrastructure, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
In 2022, Norway saw the commissioning of 25 small hydropower plants, with a combined capacity of 163 megawatts (MW) and an anticipated annual production of 530 gigawatt-hours (GWh). These new additions to the hydropower infrastructure are contributing to the country’s renewable energy generation, enhancing its capacity for clean and sustainable electricity production.
Paris Agreement: Advancing Global Climate Action through Renewable Energy Solutions
The Paris Agreement stands as a pivotal international accord in the global fight against climate change. Its core objective is to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, with an aspiration to cap the increase at 1.5 degrees Celsius.
A significant strategy within the Paris Agreement is the encouragement of renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, to replace carbon-intensive fossil fuels. These clean energy alternatives help nations drastically reduce their carbon emissions and transition to an environmentally sustainable energy landscape.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Practical Strategies for a Greener Planet
Curbing the emissions of greenhouse gases is vital for combating climate change. By implementing effective strategies, we can make a real difference in preserving the planet. Let’s explore these strategies and their global examples.
Boosting Energy Efficiency

- Improving Building Efficiency: Across the globe, cities like New York and London are retrofitting buildings with energy-efficient technologies to reduce emissions. Upgrading insulation, using LED lighting, and optimizing heating and cooling systems all contribute to lower energy consumption.
- Enhancing Industrial Efficiency: Countries like Germany and Japan have championed industrial energy efficiency, reducing emissions in manufacturing processes. They’ve adopted advanced technologies and innovative practices to make industries more environmentally friendly.
Transitioning from Fossil Fuels
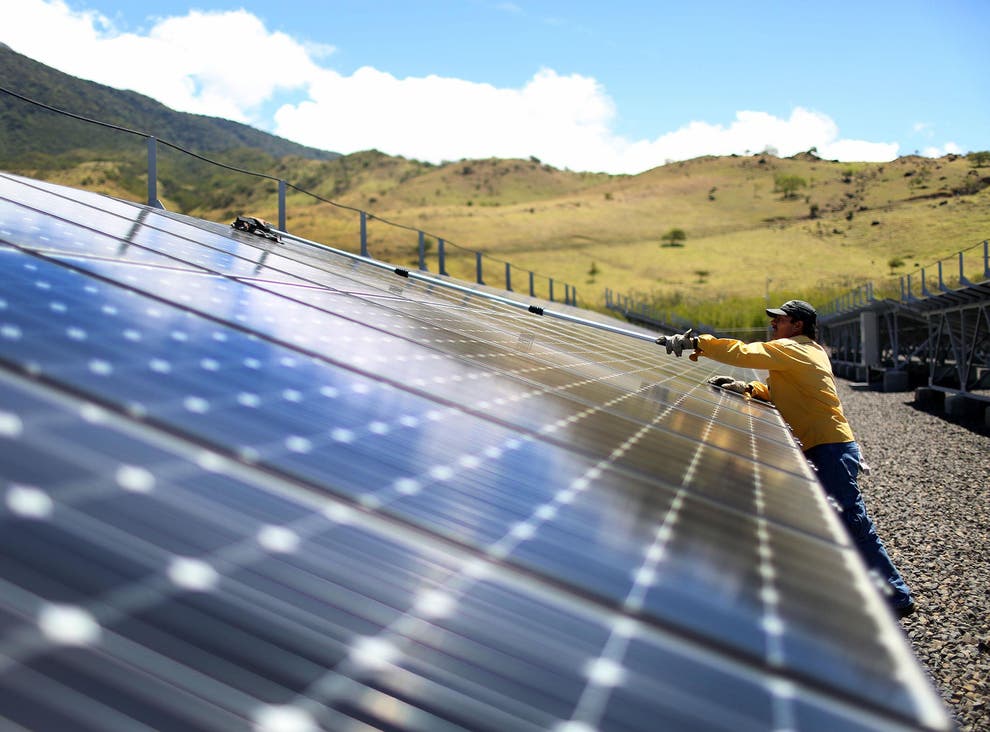

- Investing in Renewable Energy: Countries like Denmark and Costa Rica are at the forefront of renewable energy adoption. Denmark’s wind farms and Costa Rica’s hydropower plants demonstrate how transitioning from fossil fuels to clean energy can significantly reduce emissions. As per Costa Rica’s National Energy Control Center (CENCE), in 2022, Costa Rica could produce 98.53% of its electricity using five renewable sources over the past four years.
- Advancing Cleaner Technologies: Research and development in alternative energy sources are essential. Innovations like Tesla’s electric vehicles and advancements in solar technology are making cleaner energy options more accessible.
Promoting Sustainable Transportation
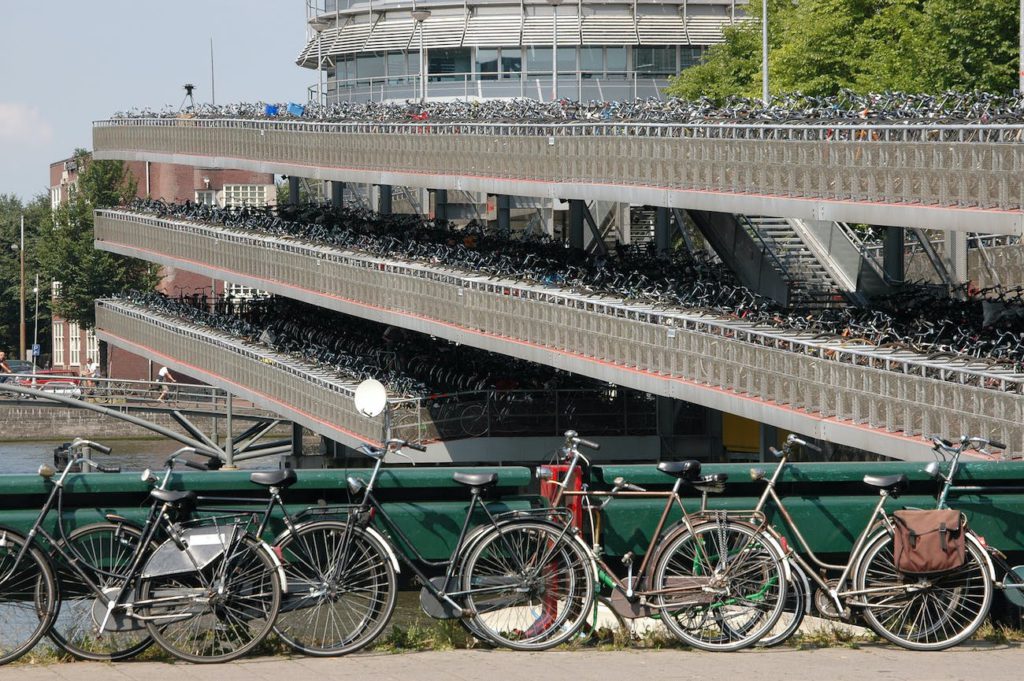

- Encouraging Biking and Walking: Cities like Amsterdam and Copenhagen are renowned for their bike-friendly infrastructure, reducing the need for cars and decreasing emissions. In the 1970s, Copenhagen residents protested at City Hall, urging authorities to prioritize cycling alongside the car. Their efforts led to the inclusion of bicycles in city planning, resulting in a steady rise in cycling over the years. In 2018, nearly half of trips to work and education were by bike, and in the inner city, bicycles outnumbered cars in 2016.
- Electric Public Transportation: Cities like Shenzhen in China have substantially invested in electric buses, reducing carbon emissions from public transportation. This approach lowers the environmental impact of mass transit.
By adopting these strategies and taking inspiration from global examples, we can collectively reduce greenhouse gas emissions and work towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Silvopasture’s Role in Combating Climate Change: A Greener Future
Silvopasture, a sustainable land management practice, holds the potential to contribute significantly to the fight against climate change. This integrated approach, which combines trees, forage crops, and livestock on a single piece of land, offers a range of environmental benefits and global examples that illustrate its positive impact.
Environmental Benefits of Silvopasture
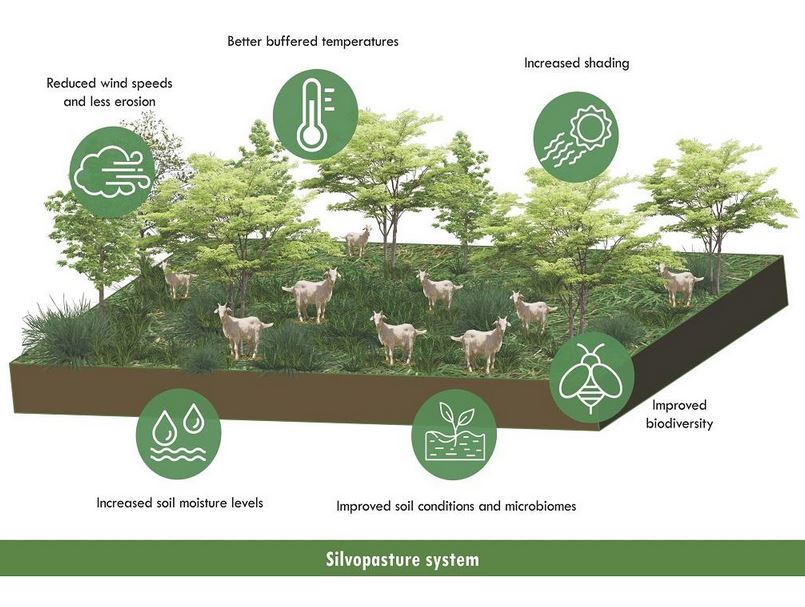
- Carbon Sequestration: Trees planted in silvopasture systems capture and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This reduces the levels of greenhouse gases responsible for global warming. An excellent example is the extensive use of silvopasture in sub-Saharan Africa, where acacia trees are integrated with livestock farming, effectively sequestering carbon.
- Wildlife Habitat: Silvopasture systems provide valuable habitat for wildlife, including birds, insects, and small mammals. In Brazil’s Amazon rainforest, indigenous communities employ silvopasture to support sustainable agriculture and preserve essential wildlife habitats.
- Soil Health and Fertility: The presence of trees enhances soil health and fertility. The United States showcases successful silvopasture systems, particularly in the southeastern region, where the integration of trees with livestock has led to improved soil quality.
- Extreme Weather Mitigation: Silvopasture can help mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events. In the Philippines, farmers are using silvopasture systems to reduce soil erosion during heavy rainfall and to provide shade and shelter for livestock in high temperatures.
Challenges and Considerations
- Planning and Management: Establishing and maintaining silvopasture systems requires careful planning and management. In South Asia, countries like India address these challenges by promoting best practices for silvopasture management.
- Economic Viability: The economic viability of silvopasture may vary based on factors such as location, scale, and market demand for products. Governments and organizations worldwide are exploring financial incentives to make silvopasture more economically attractive.
Silvopasture, with its ecological and climate benefits, represents a valuable solution in the global effort to combat climate change. As regions worldwide adopt and adapt these systems, they contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future for our planet
Climate Models: Guiding Climate Action for a Sustainable Future
Climate models are instrumental tools in the global efforts to combat climate change. They serve to understand the intricate workings of Earth’s climate system, predict future scenarios, and assist in making informed decisions and policies. Let’s explore the significance of climate models, their predictions, limitations, and their role in shaping policies worldwide.
The Significance of Climate Models
Climate models are essential in deciphering the complex web of factors contributing to climate change. By simulating various interactions, including greenhouse gas emissions, atmospheric conditions, and land use changes, these models provide valuable insights into how the climate system functions.
Predictions and Their Real-world Implications
Climate models make predictions about future climate scenarios, enabling us to anticipate the consequences of our actions. For instance, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) uses a suite of climate models to project future climate outcomes based on different greenhouse gas emission scenarios. These projections guide the global community in understanding the urgency of reducing emissions to limit global warming.
Acknowledging Limitations
It’s crucial to recognize that climate models have limitations. Uncertainties in their projections arise from factors like incomplete data, simplifications of complex processes, and the inherent unpredictability of natural phenomena. These uncertainties require a cautious approach to interpreting model results.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, some solutions can help reverse global warming and slow climate change.
Some solutions include reducing emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, carbon removal technologies, and efforts to reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
Reducing emissions refers to reducing the amount of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, released into the atmosphere.
Renewable energy sources like wind and solar power produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, thereby reducing the carbon footprint and helping to slow climate change.
Carbon removal is capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, effectively removing it and reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases.
While it may be difficult to completely stop global warming, implementing sustainable practices, reducing carbon dioxide emissions, and pursuing carbon removal technologies can help mitigate its effects.
Reversing the earth’s temperature to pre-industrial levels is challenging, as it would require significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and large-scale carbon removal efforts.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is a scientific body established by the United Nations to provide policymakers with relevant scientific information on climate change.
Climate change poses significant risks to the world’s arable land, as extreme weather events, rising temperatures, and changing precipitation patterns can reduce agricultural productivity.
While some impacts of climate change may be irreversible, taking action to reduce emissions and slow down its progression can help mitigate the long-term effects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the prospect of reversing climate change and mitigating global warming is within our grasp. By exploring and implementing a spectrum of innovative solutions, from transitioning to clean energy sources to sustainable land management practices and informed policy decisions, we can collectively address the pressing challenges of our time.
While the road ahead is not without its hurdles and complexities, the global community’s commitment to sustainability, combined with the remarkable strides already made, paints a promising picture. With ongoing dedication and cooperation, we can strive to reverse climate change, protect our planet, and secure a more sustainable and vibrant future for future generations.