|
|
In energy sources and their environmental implications, few topics ignite as much controversy as natural gas. As a fossil fuel, natural gas has witnessed a surge in popularity in recent times, primarily owing to its portrayal as a cleaner option compared to other fossil fuels.
Yet, apprehensions linger regarding the environmental repercussions linked to the entire natural gas lifecycle, from production and transportation to combustion. In the following article, we embark on a comprehensive journey to unravel the multifaceted dimensions of natural gas and its intricate relationship with the environment.
What is Natural Gas?
Natural gas, mainly composed of methane, provides roughly 30% of U.S. energy. Around 40% is used for making electricity, while the rest serves homes, businesses (for heating and cooking), and industries. However, very little, just 0.2%, is utilized for transportation fuel.
How Is Natural Gas Extracted?
Obtaining natural gas through hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, is a complex process to access this valuable energy source trapped deep within the Earth’s crust. Here’s an expanded look at the key steps involved:
- Well Drilling: The process begins with the drilling of a well deep into the Earth, often extending thousands of feet below the surface. Once the well reaches its target depth, it may turn horizontally to intersect natural gas-rich rock formations.
- Injection of Fluids: A high-pressure fluid mixture is prepared, consisting of water, sand, and a blend of chemicals. This mixture is crucial for fracturing the rock and releasing the trapped gas. When injected into the well, the powerful force created by the pressurized fluid initiates fractures within the rock layers.
- Gas Release: As the rock formations crack and fracture, the natural gas within these geological structures is released and flows into the wellbore. The injected sand, which is called proppant, helps to keep these fractures open, allowing gas to escape more freely.
- Extraction and Collection: The freed natural gas is then brought to the surface, which is collected and transported for further processing and distribution.
The Role of Natural Gas in Energy
Natural gas is a crucial player in the world’s energy sector. It serves various purposes, from generating electricity and heating homes to fueling vehicles and cooking. It stands out because of its lower carbon dioxide emissions than coal and oil, making it an environmentally friendlier energy source.
What are the Environmental Impacts of Natural Gas?
How does natural gas contribute to climate change?
Natural gas is a fossil fuel, and its combustion releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. The gases people emit, like carbon dioxide, are a big reason for climate change, which is a major worldwide problem. This connection between how warm the Earth gets and the gases we release, especially carbon dioxide, has existed for a long time in Earth’s history.
The chart shows how much temperatures differ from the average temperatures between 1961 and 1990. If the chart shows a positive number, it means the temperature is higher than the average during that period, and if it’s negative, it’s lower. This information is available for the Northern Hemisphere (the top half of the Earth) and the Southern Hemisphere (the bottom half).
To find the average temperature change for the entire planet, they add up the temperature differences from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres and then divide by two. This gives us the overall global temperature change.
What are the greenhouse gas emissions associated with natural gas production?
In addition to carbon dioxide, the extraction and production of natural gas can result in the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Methane has a much higher heat-trapping potential than carbon dioxide, making it a significant contributor to climate change. Methane emissions can occur during extraction, transportation, and natural gas storage.
Is natural gas a cleaner alternative to other fossil fuels?
While natural gas has lower carbon emissions compared to coal and oil, it is still a fossil fuel and contributes to climate change. Its classification as a “cleaner” fuel is relative to more carbon-intensive sources. The shift towards renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power is necessary to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Does Natural Gas Cause Air Pollution?

What are the air pollutants released during natural gas combustion?
Although natural gas produces lower levels of air pollutants than other fossil fuels, it is not entirely emissions-free. Combustion of natural gas can result in the release of nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These pollutants can contribute to smog formation and negatively impact air quality and human health.
How does natural gas extraction contribute to air pollution?
In addition to the pollutants released during combustion, the extraction process can contribute to air pollution. Methane leakage during hydraulic fracturing operations has been a concern, as methane is a powerful greenhouse gas and can also contribute to local air pollution.
What are the health impacts of natural gas emissions on respiratory health?
The emissions associated with natural gas combustion can harm respiratory health. Nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds are known to contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, which can irritate the respiratory system and exacerbate conditions such as asthma and other respiratory diseases.
A study called the Global Burden of Disease found that in 2019, 4.14 million people died from this outdoor air pollution. That’s a lot of lives affected.
Death rates from pollution are measured as the number of deaths caused by pollution for every 100,000 people. These rates are adjusted for age, which means they consider that the age distribution of the population remains constant. This adjustment is necessary because it allows us to compare pollution-related death rates between countries and periods. In simple terms, it levels the playing field for fair comparisons.
What are the Potential Risks of Natural Gas Infrastructure?
What are the environmental concerns associated with natural gas pipelines?
Natural gas pipelines are essential for transporting gas from production sites to end-users. However, the construction and operation of pipelines can have environmental implications. Pipeline leaks can release methane into the atmosphere and risk local ecosystems.
How does natural gas transportation contribute to methane leakages?
The transportation of natural gas through pipelines and other means can result in methane leakages. Methane leakage is a concern because it has a higher heat-trapping potential than carbon dioxide and contributes to climate change. Reducing methane emissions from transportation infrastructure is crucial for mitigating the environmental impact of natural gas.
What are the risks of natural gas storage facilities?
Natural gas is often stored in underground facilities for later use. These storage facilities can pose risks such as leaks and explosions, which can have environmental and safety implications. Ensuring the integrity and safety of natural gas storage is essential to minimize potential risks.
Is Natural Gas a Bridge Fuel to Renewable Energy?
What is the role of natural gas in transitioning to renewable energy sources?
Natural gas is often touted as a “bridge fuel” that can help transition from more carbon-intensive fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. As a cleaner-burning fuel, natural gas can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to coal and oil. However, this transition must be accompanied by a shift towards renewable energy sources to address the climate crisis effectively.
Are there any limitations to using natural gas as a bridge fuel?
While natural gas can serve as a bridge fuel, it is not a long-term solution to the climate crisis. Continued reliance on natural gas without a concurrent investment in renewable energy technologies will only delay the necessary transition. Furthermore, the extraction and production of natural gas have their environmental concerns that must be addressed.
How does natural gas impact the development of renewable energy technologies?
Natural gas can impact the development of renewable energy technologies in various ways. On one hand, the availability and affordability of natural gas can compete with renewable energy sources, potentially slowing down their deployment. However, the flexibility provided by natural gas power plants can also complement the intermittent nature of renewable energy from wind and solar power.
Environmental Concerns and Critics
While hydraulic fracturing has significantly expanded the accessibility of natural gas, it has also raised environmental concerns and faced criticism:
Groundwater Contamination: One primary concern is the potential for the chemicals used in the fracking fluid to migrate into underground drinking water sources. Instances of groundwater contamination have been reported in various regions.
Wastewater Management: Disposing water produced during fracking, which contains not only the original fracking fluids but also naturally occurring contaminants from the rock formations, is another environmental challenge. Managing this wastewater safely remains a critical issue.
The chart spans from 2000 to 2020, enabling long-term trend assessment of hazardous waste generation on a per capita basis. We can track whether waste production has increased, decreased, or remained steady during this period, identifying key policy changes and environmental effects. Understanding these implications is vital for informed action in waste management. Comparative analysis between countries or regions may provide insights into successful waste reduction approaches.
Community Impacts: Fracking, short for hydraulic fracturing, is frequently conducted in or close to neighborhoods, raising concerns about its impact on local communities. These concerns include noise pollution from drilling operations and the constant flow of trucks transporting equipment and materials. The presence of fracking activities can disrupt the peace and well-being of communities, affecting the quality of life for residents.
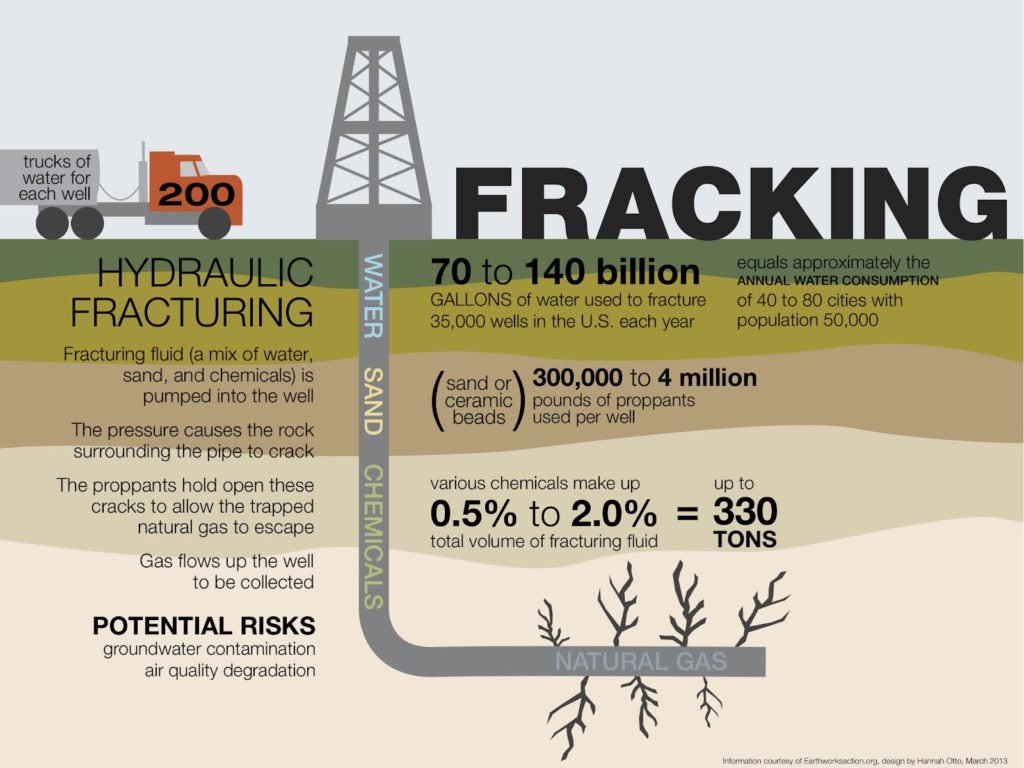
Image Credit: truthinsideofyou.org
In the United States, Pennsylvania and Texas have experienced significant fracking activities. In Pennsylvania, rural communities have voiced concerns about the noise generated by drilling operations, as well as the increased truck traffic on narrow country roads.
In Texas, where fracking is expected in the Permian Basin, the growth of oil and gas activities has led to worries about the impact on the local way of life, including the pressure on housing and infrastructure.
These community impacts highlight the need for careful consideration and regulation of fracking to minimize disruptions and protect the well-being of residents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the exploration of the environmental impacts of natural gas reveals a complex picture. While natural gas offers advantages such as lower carbon emissions compared to coal and oil, it has drawbacks. Its extraction and production can result in methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas, and hydraulic fracturing, or fracking has raised concerns about groundwater contamination.
Understanding these complexities is essential for informed decision-making regarding energy sources and climate change mitigation. As the world seeks cleaner, sustainable energy options, the role of natural gas in the transition remains debatable. Balancing its benefits with environmental consequences is a crucial challenge as we work towards a more sustainable and greener future.