|
|
In today’s rapidly evolving world, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to thrive and prosper. The concept of a circular economy has emerged as a game-changer in the pursuit of sustainable business practices, offering a fresh perspective on resource management and waste reduction.
As concerns surrounding environmental degradation and resource scarcity become increasingly pressing, the necessity for businesses to adopt circular models is more significant than ever.
The circular economy concept is centered around the idea of designing out waste, promoting the continual use of resources, and regenerating natural systems. This transformative approach can significantly impact business sustainability by extending product lifecycles, harnessing renewable energy sources, and fostering collaborative consumption.
The article below explores the intricacies of the circular economy and its implications on business sustainability. Read on to learn how you can integrate circularity into your own business operations and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Key Takeaways
- Circular economy, focusing on waste reduction and resource efficiency, directly enhances business sustainability.
- The circular economy principles include reduction, reuse, and recycling, supported by innovative product design and business models.
- Adopting circular practices can bring cost savings, enhance brand reputation, and stimulate innovation, despite initial investment challenges.
- Product-as-a-service and collaborative consumption models enable circularity by extending product lifecycles and optimizing resource use.
- Measuring circular initiatives’ impact through specific KPIs can highlight areas for improvement and track sustainability goals.
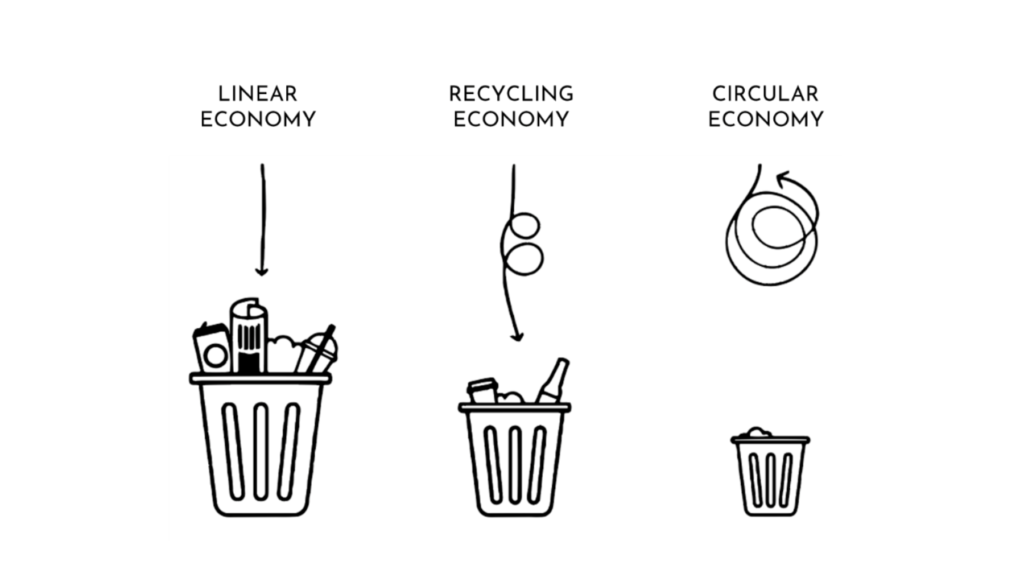
Image source: https://www.chooseanew.com/blogs/news/linear-vs-circular-economy-whats-the-difference
Understanding the Circular Economy: Key Principles and Components
The circular economy is a paradigm shift from the traditional linear model of “take, make, and dispose” to a sustainable and regenerative approach that focuses on minimizing waste, maximizing resource efficiency, and fostering a closed-loop system.
The concept is grounded in three key principles: reduce, reuse, and recycle:
- Reduce. This principle emphasizes the importance of using fewer resources and materials in the production process while maintaining product quality and functionality. This can be achieved through innovative design, increased energy efficiency, or by opting for renewable energy sources.
- Reuse. Prolonging the life of products and materials is at the core of this principle. Companies can incorporate modularity, repairability, and upgradability into their product designs, thereby ensuring that items can be easily refurbished, repurposed, or remanufactured for extended use.
- Recycle. The final principle focuses on recovering valuable materials from discarded products and reintegrating them into new production cycles. Effective recycling processes not only minimize waste generation but also reduce dependency on virgin materials, conserving natural resources.
In addition to these principles, the circular economy comprises several essential components:
- Product design. Designing products with circularity in mind ensures longevity, ease of maintenance, and recyclability. Products should be durable, modular, repairable, and made from recycled or renewable materials whenever possible.
- Business models. Innovative business models support the circular economy by encouraging resource optimization and waste reduction. Examples include product-as-a-service models, sharing platforms, and take-back schemes that incentivize customers to participate in circular practices.
- Collaboration. Successful implementation of a circular economy requires cross-sector collaboration among businesses, governments, non-profit organizations, and consumers. This cooperation facilitates the development of supportive policies, infrastructure investments, and shared knowledge to drive circular innovation.
- Education and awareness. Raising awareness about the benefits and practices of a circular economy is vital for driving change. This involves educating consumers about responsible consumption choices, engaging employees in sustainable practices, and promoting transparency within the supply chain.
By understanding these key principles and components, businesses can leverage the circular economy to create value, enhance sustainability, and contribute to a more resilient future.
The Role of Circular Economy in Business Sustainability
The adoption of circular economy practices directly contributes to enhanced business sustainability.
For instance, thanks to conserving resources and reducing waste, businesses can decrease their ecological footprint and mitigate environmental risks. This approach also fosters economic resilience by reducing dependency on finite resources and tapping into new revenue streams through innovative business models such as product-as-a-service or collaborative consumption platforms.
Embracing circular practices can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty as consumers become more environmentally conscious and seek sustainable products.
Product-as-a-Service (PaaS)
In the PaaS model, businesses retain ownership of their products and offer the benefits of the product as a service to customers. Instead of selling the product outright, the company leases or rents it to the customer for a specified period.
This model incentivizes businesses to create durable, high-quality products that can be used for a long time, and it facilitates reuse and recycling when products reach the end of their service life.
An example might be a company like Michelin, which provides tires-as-a-service to commercial truck fleets. Instead of purchasing tires, businesses pay Michelin based on the distance driven.
Michelin maintains, repairs, and, when necessary, replaces the tires. As the owner of the tires, Michelin is incentivized to manufacture long-lasting, durable tires and recycle them at the end of their life cycle.
Collaborative Consumption Platforms
Some platforms facilitate the sharing, swapping, trading, or renting of goods and services between peers, often enabled by digital technology. These platforms can contribute to a circular economy by extending the useful life of products and making more efficient use of resources.
Examples of such platforms are Airbnb (sharing of homes), Uber (sharing of rides), or ThredUp (reselling of clothes). By allowing individuals to share access to goods or services, this model reduces the need for ownership and the demand for the production of new items, thereby reducing the resource footprint.
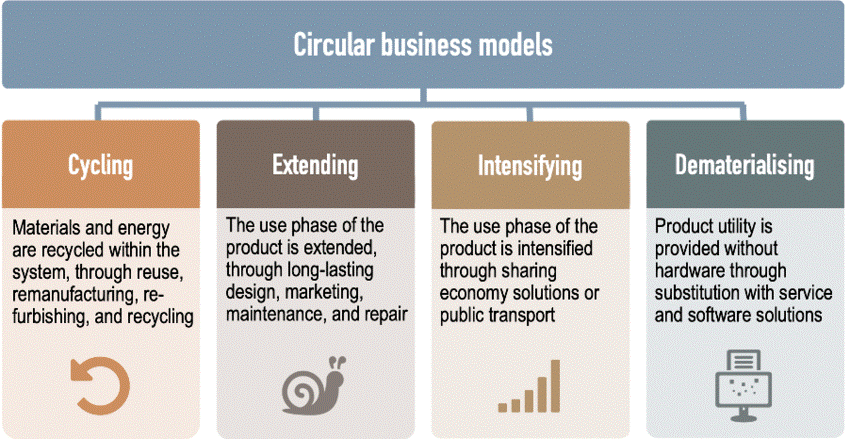
Image source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Circular-business-model-strategies_fig4_343810965
Challenges and Opportunities in Adopting Circular Business Models
Adopting circular business models presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses looking to transition from traditional linear approaches to more sustainable and regenerative practices. Below are some of the key challenges and the corresponding opportunities that arise from embracing circularity in business operations
Challenges
- Initial investment. The shift towards a circular business model often requires significant upfront investments in redesigning products, establishing new infrastructure, and rethinking overall business processes. This can be a barrier, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited financial resources.
- Resistance to change. Transitioning to a circular economy involves changes at every level of an organization, which can be met with resistance from employees, suppliers, and customers who are used to conventional practices. Overcoming this inertia is vital for successful implementation.
- Market dynamics. Circular business models may face challenges in competing against established linear models due to market pressures, consumer preferences, or regulatory frameworks that favor traditional approaches.
- Supply chain complexity. Integrating circular principles into complex global supply chains can be challenging, as it requires cooperation and coordination among multiple stakeholders with varying levels of commitment to sustainability.
Opportunities
- Cost savings and resource efficiency. Adopting circular practices can lead to long-term cost savings by reducing resource consumption, waste disposal costs, and reliance on finite resources. This also contributes to increased resilience against fluctuations in commodity prices and supply chain disruptions.
- Innovation and differentiation. Embracing circularity promotes innovation in product design, materials, and business models, giving companies a competitive edge and the potential to capture new markets.
- Brand reputation and customer loyalty. As consumers become increasingly environmentally conscious, businesses that adopt circular practices can enhance their brand image and attract loyal customers who seek out sustainable products and services.
- Collaboration and partnerships. The transition to a circular economy encourages collaboration between businesses across sectors, fostering symbiotic relationships that optimize resource use while creating new revenue streams. Partnerships with governments, non-profits, and research institutions can also facilitate the development of supportive policies and infrastructure for circularity.
Strategies for Integrating Circular Economy Principles in Your Business
Integrating circular economy principles into your business requires a strategic approach that focuses on redesigning processes, fostering innovation, and engaging stakeholders.
Here are some strategies to help you successfully incorporate circularity into your operations:
- Conduct a comprehensive assessment. Begin by analyzing your current practices and identifying areas where waste can be reduced or resources can be conserved. Pinpoint opportunities for improvement and prioritize initiatives based on their potential impact on sustainability and business performance.
- Set clear goals and targets. Establish specific, measurable, and achievable targets related to waste reduction, resource efficiency, and circularity. Align these goals with your overall business strategy and ensure they are communicated effectively throughout the organization.
- Design products for circularity. Focus on creating products that are durable, modular, repairable, and made from renewable or recycled materials. This will enable easy refurbishment, repurposing, and recycling at the end of their lifecycle, contributing to waste reduction and resource conservation.
- Adopt innovative business models. Explore alternative models that support circular practices, such as product-as-a-service, sharing platforms, or take-back schemes. These approaches can generate new revenue streams while promoting resource optimization and waste reduction.
- Engage stakeholders. Actively involve employees, suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders in your transition toward a circular economy. Encourage feedback, share best practices, and foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement to ensure circular practices are embedded throughout the organization.
- Communicate your commitment. Share your sustainability goals, achievements, and challenges with stakeholders through transparent reporting and marketing efforts. This not only builds trust but also positions your brand as a leader in sustainability.
- Offer employee training and development. Provide training on circular economy principles and practices to employees, enabling them to contribute effectively to your organization’s sustainability objectives. Encourage skill development that supports circular processes, such as repair, refurbishment, or remanufacturing.
By implementing these strategies, you can successfully integrate circular economy principles into your business operations, fostering long-term resilience, competitiveness, and sustainability.
Measuring the Impact of Circular Initiatives on Business Performance
To evaluate the success of your circular initiatives, establish clear metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that are aligned with your sustainability goals. These may include but are not limited to:
- waste reduction rates,
- resource consumption levels,
- product lifecycle extension percentages,
- revenue generated from circular business models.
Regularly track and analyze performance data to identify areas for improvement and celebrate successes. Sharing these achievements with stakeholders can further enhance your brand reputation and demonstrate your commitment to sustainability.
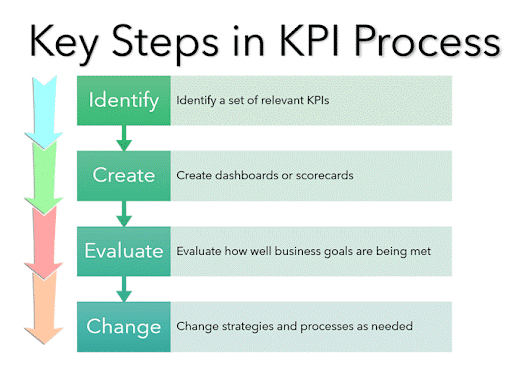
Image source: https://www.ringcentral.com/gb/en/blog/definitions/kpi-key-performance-indicators/
In Conclusion
As global environmental challenges continue to escalate, the adoption of circular economy principles becomes increasingly vital for businesses seeking long-term resilience and success. By embracing this transformative approach, companies can not only reduce their environmental impact but also unlock new economic opportunities and enhance their competitive advantage.
As more businesses adopt circular practices, a systemic shift towards a sustainable, regenerative economy will emerge, fostering long-term prosperity for both businesses and the planet.