|
|
The world’s population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050 and almost 11 billion by the end of the century. As our planet’s population grows, so do the challenges we face in terms of resource consumption, environmental degradation, and social inequality.
Understanding the projections and data surrounding future population growth is critical for policymakers, researchers, and citizens alike.
This article will delve into the fascinating and complex world of population projections and data, exploring the factors that contribute to population growth and decline and the implications of these trends for our future.
We will examine how population projections are made, what variables are taken into account, and how they can be used to inform policy decisions.
Whether you’re a demographer, a policy wonk, or simply someone interested in the world around you, this article promises an engaging and informative deep dive into the fascinating world of future population projections and data.
What Are Population Predictions and How Are They Made?
Population predictions, or population projections, are estimates of the future size and composition of a population. They are essential tools for policymakers, researchers, and businesses that rely on demographic information to make informed decisions.
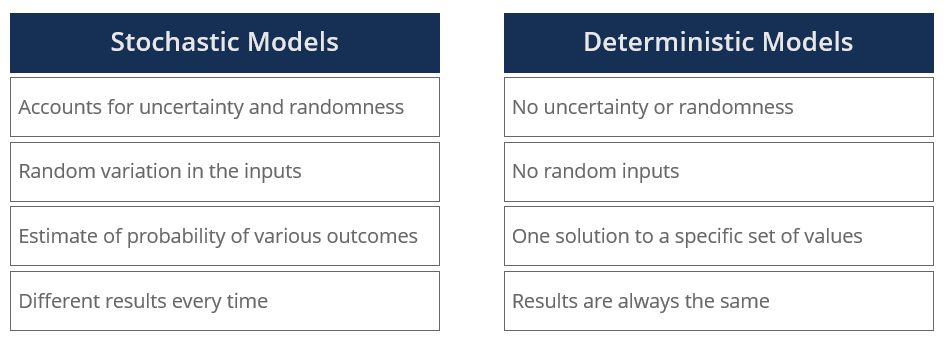
Population projections are made using mathematical models that take into account various factors such as birth rates, death rates, migration patterns, and aging trends. These models can be either deterministic or stochastic.
source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/data-science/stochastic-modeling/
Deterministic models are based on assumptions about future trends in fertility, mortality, and migration. They assume that these trends will continue unchanged into the future and provide an exact outcome.
Stochastic models, on the other hand, incorporate uncertainty into the projections by allowing for random variations in the inputs.
To make population projections, demographers use data from censuses, surveys, and administrative records to estimate current population size and characteristics. They then apply assumptions about future fertility, mortality, and migration rates to project the population forward in time.
The accuracy of population projections depends on the quality of the data used to make them and the validity of the assumptions about future trends.
Demographers often make multiple projections using different assumptions to account for uncertainty and to explore different policy scenarios.
What Are the Projections for Future Population Growth?
source: https://ourworldindata.org/future-population-growth
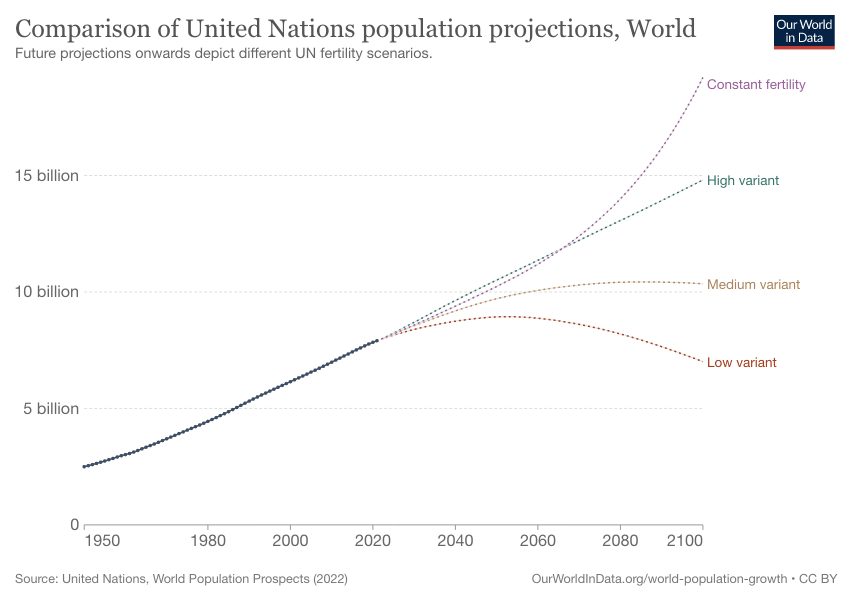
According to the United Nations, the world’s population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050 and almost 11 billion by the end of the century. These projections are based on assumptions about future trends in fertility, mortality, and migration.
The rate of population growth is expected to vary significantly across different regions of the world.
In high-income countries, population growth is expected to be relatively slow, with some countries experiencing population decline due to low fertility rates. In contrast, population growth in low-income countries is expected to be much faster due to high fertility rates and improved healthcare.
The population of Africa, in particular, is expected to grow rapidly over the next few decades, with the continent’s population projected to double by 2050.
In addition to regional differences, population projections also show significant variations in population age structure.
Many high-income countries are expected to experience population aging, with increasing numbers of older people and declining numbers of younger people.
This can lead to significant social and economic challenges, including increased demand for healthcare and social welfare programs.
What Factors Contribute to Population Growth and Decline?
Population growth or decline depends on several factors, including fertility, mortality, and migration. These factors can vary significantly across countries and regions, leading to differences in population growth rates.
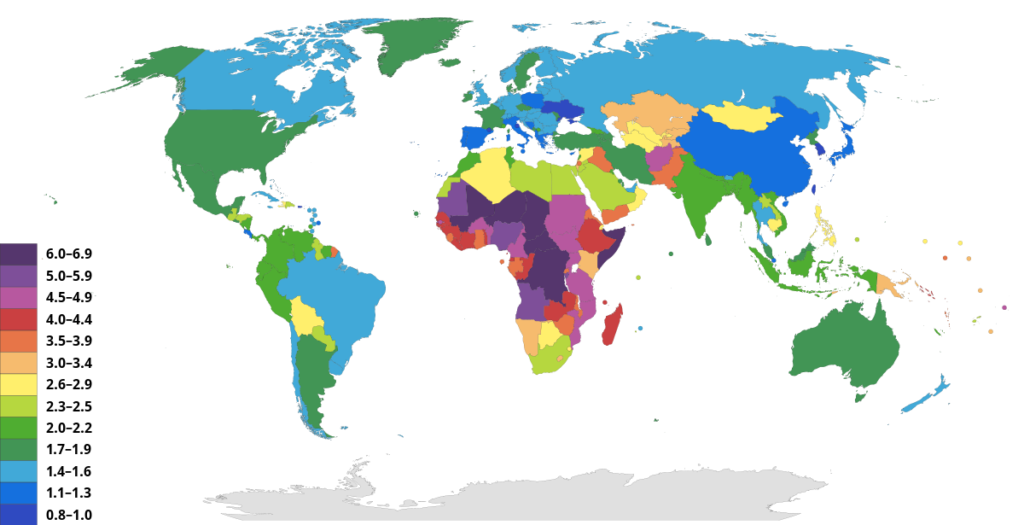
Fertility rates are one of the most significant determinants of population growth. In general, a fertility rate of 2.1 children per woman is considered the replacement level fertility rate – the level at which a population replaces itself from one generation to the next without migration.
Fertility rates around the world:
source: Population Reference Bureau
Fertility rates above 2.1 lead to population growth, while rates below 2.1 lead to population decline.
Mortality rates also play a role in population growth or decline. Improvements in healthcare, nutrition, and sanitation have led to significant reductions in mortality rates in many parts of the world, leading to population growth.
However, in some countries, mortality rates remain high due to poverty, war, or disease, resulting in population stagnation or decline.
Migration can also affect population growth or decline. In general, immigration increases population growth while emigration decreases it, though the effects vary by country and the magnitude of the migration flows.
You can read more about Earth’s population growth factors here.
What Do Population Projections Tell Us?
Population projections provide policymakers, researchers, and businesses with valuable information about the future size and composition of populations. They can help anticipate future demand for healthcare, education, housing, and other services and plan accordingly.
These predictions can also be used to inform policy decisions related to immigration, family planning, and social welfare programs. For example, projections that show an aging population can help design retirement and healthcare programs that are sustainable in the long term.
They will also be helpful in anticipating future environmental challenges. As populations grow, they consume more resources, generate more waste, and contribute more to climate change. Population projections can help policymakers and researchers anticipate future demand for resources and plan accordingly.
The Impact of Population Growth on the Environment
Population growth has significant implications for the environment, including increased resource consumption, deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
As populations grow, they require more resources, including food, water, energy, and land. This can lead to overuse and depletion of natural resources, resulting in environmental degradation.
For example, overfishing and pollution have led to declines in fish populations, while deforestation – to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
Population growth can also mean an increase in pollution – both air and water pollution. This can have significant health consequences, such as respiratory and cardiovascular disease.
Climate change is another significant environmental effect of population growth. As populations grow, they generate more greenhouse gas emissions, leading to increased global warming.
This can have a range of consequences, including rising sea levels, more frequent and severe weather events, and changes in ecosystem dynamics.
You can read more about how population affects the environment here.
The Impact of Population Growth on Social Systems
Population growth can also have significant implications for social systems, i.e., urbanization, migration, and inequality.
As populations grow, people tend to move to urban areas in search of better economic opportunities. This can culminate in overcrowding, poverty, and social inequality, as well as increased demand for infrastructure and services.
Migration is another significant social consequence of population growth. As populations grow, people may migrate from poorer to richer countries in search of better economic opportunities.
This can create social tensions and conflicts, particularly if there are disparities in wealth and resources between the sending and receiving countries.
Population aging is another social consequence of population growth, particularly in high-income countries. As the population ages, there may be increasing demand for healthcare and social welfare programs, which can place significant strains on social systems.
The Impact of Population Growth on the Economy
Population growth can have major economic implications, including changes in labor force participation, productivity, and economic growth.
As the population grows, there may be more people entering the labor force, resulting in an increase in economic output. However, if the economy does not grow at the same rate as the population, it can lead to unemployment and stagnant economic growth.
Population growth can also lead to changes in productivity as new technologies and innovations are developed to meet the demands of a growing population. But if the population grows too quickly, there may be a strain on resources and infrastructure, which will reduce productivity.
In addition, population growth can lead to changes in consumer behavior, with increased demand for goods and services. This can create new business opportunities, but it can also result in increased competition and pressure on prices.
Conclusion
Population projections and data are critical tools for understanding the challenges and opportunities associated with future population growth.
By examining the factors that contribute to population growth and decline and understanding the implications of these trends for the environment, society, and the economy, policymakers, researchers, and citizens can work together to develop strategies to mitigate the negative impacts and promote sustainable growth.
While the challenges associated with population growth are significant, they also present opportunities for innovation, creativity, and collaboration. By working together, we can create a future that is both prosperous and sustainable for generations to come.












No Comments