|
|
Human beings have been altering their surroundings since the dawn of civilization. But in the last few centuries, the pace of change has accelerated dramatically, and with it, the impact on the global environment.
While the population per se does not cause environmental damage, the human activities associated with it, such as land conversion, resource use, and pollution release, do.
As long as we don’t learn to manage the growing number of people and population density, these activities will continue to degrade the environment.
In this article, we will take a closer look at how population affects the environment. We will discuss the environmental consequences of population growth and what can be done to mitigate these effects.
Key Takeaways
- Human activities associated with population growth, such as land conversion, resource use, and pollution release, cause environmental damage.
- Population growth puts increasing pressure on the environment, leading to deforestation and land conversion, water scarcity, air pollution and global warming, and loss of biodiversity.
- Population growth puts a strain on resources, leading to resource depletion in land use, water use, energy use, food demand and agricultural practices, and extraction of minerals and non-renewable resources.
- Mitigation strategies for the impact of population growth on the environment include sustainable land use practices, renewable energy sources, sustainable transportation, responsible agriculture, sustainable food production, food waste reduction, resource conservation, and circular economies.
- Individuals and governments need to work together to find solutions to the environmental impact of population growth through actions such as investing in sustainable solutions and promoting responsible consumption and production.
Environmental Consequences of Population Growth
A growing population puts increasing pressure on the environment. Below, we examine the various aspects of this relationship.
Deforestation and Land Conversion
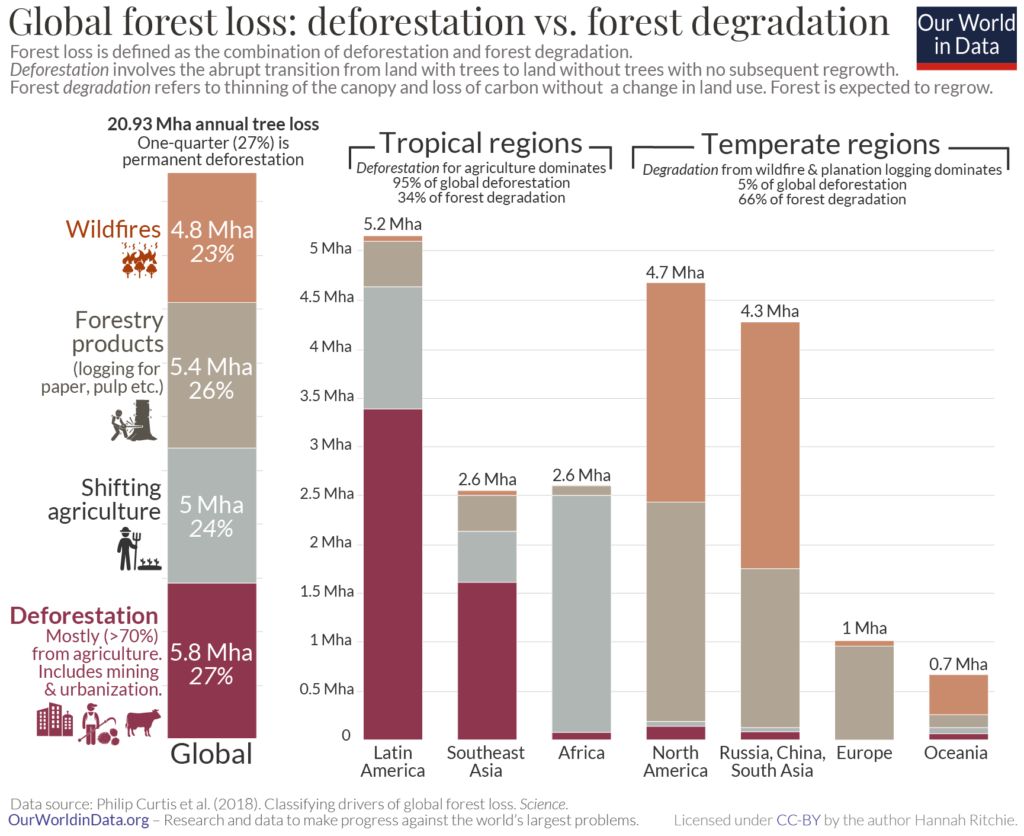
The use of land for agriculture (for growing crops, grazing cattle, and producing oil, among other activities) has dramatically impacted our environment.
Forests and grasslands have been cleared to make room for farmland, resulting in the loss of habitat for many plant species, animals as well as native peoples. The clearing has also caused major changes in soil composition and erosion rates.
Additionally, the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides has polluted streams, rivers, lakes, and oceans.
The rainforests are called “the lungs of the Earth” for a reason − they produce vast amounts of oxygen and are a large repository for carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
All these factors have upset the delicate balance that exists between our species and nature.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, in the last 30 years, our planet lost more than 420 million hectares or about a billion acres of forest.
What’s worrying is the fact that deforestation isn’t slowing down; on the contrary, it jumped by 21% in 2020. If this trend continues, we are looking at potentially catastrophic environmental consequences.
Water Scarcity
The adverse effects of population growth on our environment are not limited to land and forest; they also include water bodies.
Water scarcity is a serious global issue, with many countries struggling to provide clean drinking water for all their citizens.
As stated by UNICEF and WHO, 1 in 3 people worldwide have no access to safe drinking water, and WWF estimates that by 2025, two-thirds of the population may suffer due to water shortages.
Population-driven pollution, such as industrial waste dumping into the waterways, has further aggravated this issue. Water shortages lead to conflict over scarce resources, which in turn leads to even more environmental

source: https://populationmatters.org/food-water/
Air Pollution and Global Warming
Population growth has had an even more serious effect on air quality.
As the number of people increases, so does the production and consumption of energy sources like oil, coal, and natural gas.
Burning these fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2), a powerful greenhouse gas that traps heat in our atmosphere, leading to global warming – one of humanity’s greatest challenges right now.
The United Nations estimates that fossil fuels are responsible for 76% of all greenhouse gas emissions and almost 90% of all carbon dioxide emissions.
Furthermore, air pollution does not just affect our climate; it is also a major public health issue linked to premature death and illnesses like lung cancer, asthma, and heart disease. According to WHO, 7 million people die prematurely every year due to poor outdoor air quality.
Loss of Biodiversity
A growing population means more people competing for resources, leading to increased stress on ecosystems. This can cause species extinction: the gradual elimination of plants and animals from an area due to human activities such as deforestation or water pollution.
The loss of biodiversity has had severe consequences; it disrupts food production, affects natural habitats, and weakens soil fertility.
As stated by the WWF, we have lost 60% of global wildlife in just over 40 years – a shocking statistic that should serve as a wake-up call for everyone.
How Population Affects Resources
Population growth puts pressure on resources, leading to resource depletion. This means fewer resources are available for people to use and/or produce goods.
- Land Use: As the population grows, more land is needed for housing, industry, and agriculture. This can lead to deforestation, destruction of habitats, and soil degradation.
- Water Use: Population growth leads to an increase in water demand. This results in a greater need for irrigation (which has its own environmental impacts), as well as drilling into deeper aquifers that are difficult or impossible to replenish naturally.
- Energy Use: More people mean more energy consumption – from electricity production to heating and cooling homes and workplaces. The increased use of fossil fuels contributes significantly to climate change and air pollution issues, both locally and globally. It also increases the risk of dangerous accidents due to human error or natural disasters like oil spills or nuclear meltdowns.
- Food Demand and Agricultural Practices: The population increase leads to increased food demand. To meet this need, farmers must adopt intensive agricultural practices, such as using chemical fertilizers and insecticides, which can lead to soil pollution and water contamination.
- Extraction of Minerals and Non-Renewable Resources: The increased demand for non-renewable resources, such as oil and coal, has caused more extraction of these resources from the ground. This often leads to land degradation and can even cause sinkholes.
Mitigation Strategies for the Impact of Population on the Environment
The effects of population growth on the environment can be mitigated with a number of strategies. These include:
Sustainable Land Use Practices
Sustainable land use practices aim to use land for agricultural purposes without over-exploiting it. This involves implementing conservation methods, such as no-till farming and crop rotation.
It also requires limiting the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides to reduce water pollution. Sustainable land use also means preserving forests and grasslands, as these ecosystems are a major source of biodiversity. Reforestation is one of the best ways to offset deforestation and land destruction.
Renewable Energy Sources

Switching from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, could drastically reduce air pollution associated with population growth.
Additionally, investing in green technologies like electric vehicles or smart grids for managing electricity consumption can also help reduce the use of non-renewable resources. This way, we can minimize our carbon footprint and positively contribute to the environment.
Sustainable Transportation
The increased demand for transportation due to population growth has caused air pollution and traffic congestion.
To reduce this, governments and local authorities can invest in public transport systems such as metros, buses, and bike lanes. This way, more people will be encouraged to use sustainable means of transportation instead of relying on cars. Carpooling is also a more sustainable option.
Moreover, buses and cars can be powered by renewable energy sources, such as biofuels or hydrogen. This will further reduce our reliance on non-renewable resources.
Responsible Agriculture
Population growth puts a strain on resources and the environment, especially in developing countries.
To mitigate this, governments must invest in sustainable agriculture practices such as efficient irrigation systems, soil conservation techniques, and integrated pest management (IPM).
These approaches reduce synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which can cause water pollution. They also help to conserve soil fertility and increase crop yields with minimal harm to the environment.
Sustainable Food Production and Food Waste Reduction

source: https://www.epa.gov/land-research/farm-kitchen-environmental-impacts-us-food-waste
The increased demand for food due to population growth has caused an increase in unsustainable food production practices, such as mono-cropping and factory farming.
To reduce the environmental impact of these techniques, governments must invest in sustainable agriculture and livestock management. This includes using organic fertilizers (such as compost) instead of synthetic ones, promoting crop rotation and intercropping, and investing in animal welfare standards.
We can also reduce our ecological footprint by reducing household food waste. For example, buying only what we need at the grocery store or eating leftovers can help us cut down on unnecessary consumption.
Resource Conservation and Circular Economy
The increased demand for resources due to population growth has strained our ecosystems. To reduce this, we need to shift from linear production and consumption models towards circular ones.
Circular economies promote reusing and recycling materials in products and packaging instead of relying solely on virgin materials or synthetic inputs. This helps conserve resources while also reducing the environmental impact of production by eliminating waste at every step – from raw material extraction all the way up to disposal. With a circular economy, the materials used to make something can be reused again and again.
The Bottom Line
Population growth has seriously affected our environment – from deforestation to water scarcity, air pollution, and global warming; it affects us all in some way or another.
It is vital that we understand these impacts and work together to find solutions.
Sustainable land use, renewable energy sources, sustainable transportation, responsible agriculture and food production practices, as well as resource conservation and circular economies, can all help us mitigate the environmental impact of population growth.
Remember that change begins with each of us, but we should also pressure our governments to take action and invest in sustainable solutions.













No Comments