|
|
In a world where environmental challenges loom large, and the urgency to preserve our planet intensifies, the age-old practice of agriculture finds itself at a crossroads. As we grapple with food security, land degradation, and the mounting pressures of climate change, we need to turn to sustainable agriculture.
Prepare to witness the convergence of ancient wisdom and cutting-edge innovation as farmers and scientists unite to revolutionize the way we grow and harvest our sustenance. From the hushed whispers of permaculture to the resounding call of regenerative practices, we navigate a vibrant tapestry of techniques that nourish the earth while sating the appetites of a burgeoning global population.
Below, we unlock the secrets of agroecology, agroforestry, and the remarkable potential of precision farming. We try to uncover the delicate dance between biodiversity and resilience, as well as the profound impact sustainable agriculture can have on local communities and economies.
The principles of sustainable agriculture await your embrace, beckoning you to join the movement that cultivates a future we can truly sustain.
The Essence of Sustainable Agriculture

source: https://agfundernews.com/its-time-to-plant-the-seeds-of-growth-in-sustainable-agriculture
Sustainable agriculture represents a departure from conventional farming practices by emphasizing a holistic approach that balances productivity with ecological stewardship.
At its core, sustainable agriculture seeks to meet present-day food needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
The foundational principles that underpin this transformative approach include:
Agroecology: Fostering Resilient Farming Systems
Agroecology, a key pillar of sustainable agriculture, is rooted in the understanding of ecological principles and their application to farming.
By mimicking natural ecosystems, agroecological practices prioritize biodiversity, nutrient cycling, and natural pest management. This approach promotes the health of the ecosystem while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Farmers practicing agroecology leverage techniques such as intercropping, crop rotation, and biological pest control to create resilient farming systems.
The Power of Agroforestry: Nurturing Biodiversity and Meeting Food Demands
Agroforestry is a time-honored practice that integrates trees, crops, and livestock on the same land, maximizing productivity and environmental benefits.
By incorporating trees into agricultural landscapes, agroforestry provides multiple ecosystem services such as improved soil fertility, water retention, and habitat for beneficial organisms.
Moreover, the diverse array of tree crops and the associated biodiversity contribute to increased food security, offering a sustainable and regenerative alternative to monoculture.
Precision Farming: Merging Technology and Sustainable Practices
In an era of technological advancements, precision farming emerges as a game-changer in sustainable agriculture.
By utilizing sensors, drones, and data analytics, precision farming optimizes the use of resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
This approach enables farmers to tailor inputs precisely to the needs of their crops, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
With precision farming, sustainable agriculture embraces innovation while minimizing its ecological footprint.
Permaculture: Designing in Harmony with Nature
Permaculture, a holistic design approach inspired by natural ecosystems, takes sustainable agriculture to new heights.
Permaculture principles encourage the creation of food production systems that mimic the resilience, diversity, and self-sufficiency of natural ecosystems.
By embracing techniques such as polyculture, companion planting, and water harvesting, permaculture fosters sustainable food production while promoting ecological balance and regenerative practices.
Cultivating a Resilient Future
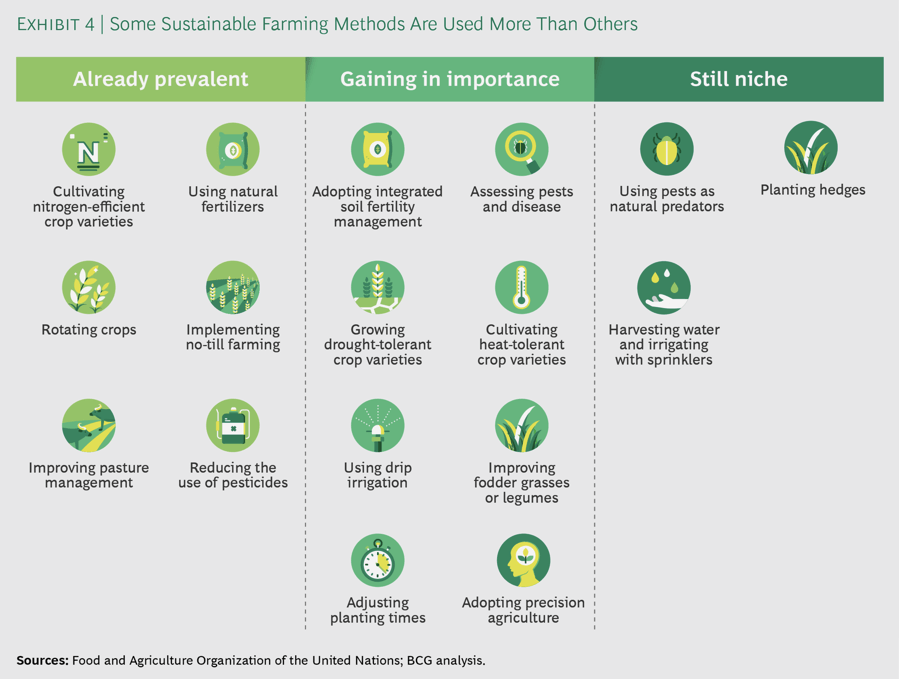
source: https://agfundernews.com/its-time-to-plant-the-seeds-of-growth-in-sustainable-agriculture
Sustainable agriculture goes beyond the principles discussed earlier and encompasses various strategies to build resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
Let us explore some key areas where sustainable agriculture plays a vital role.
Building Soil Health: The Foundation of Sustainable Agriculture
Soil health lies at the heart of sustainable agriculture.
Nurturing soil ecosystems can enhance nutrient cycling, improve water-holding capacity, and increase the resilience of their crops.
Sustainable soil management practices, such as organic farming, cover cropping, and conservation tillage, promote soil health and reduce erosion.
The adoption of these practices not only benefits crop yields but also contributes to carbon sequestration, mitigating climate change.
Water Conservation and Efficient Irrigation Strategies
Water scarcity is a growing concern, making efficient water management essential in sustainable agriculture.
Practices such as drip irrigation, precision irrigation scheduling, and rainwater harvesting optimize water use while reducing waste.
Furthermore, the implementation of agroecological approaches, such as contour farming and agroforestry, aids in water retention and minimizes runoff, preserving this valuable resource.
Climate-Smart Agriculture: Mitigating the Impact of Climate Change
Climate change poses significant challenges to agricultural systems worldwide.
Sustainable agriculture embraces climate-smart practices that help mitigate and adapt to changing climatic conditions.
Techniques such as agroforestry, conservation agriculture, and the use of climate-resilient crop varieties contribute to increased agricultural productivity and the resilience of farming systems in the face of extreme weather events and shifting climatic patterns.
Embracing Regenerative Practices: Restoring Ecosystems and Revitalizing Communities
Regenerative practices take sustainable agriculture a step further, aiming not only to minimize harm but to actively restore ecosystems and revitalize communities.
Regenerative agriculture focuses on building soil organic matter, enhancing biodiversity, and fostering carbon sequestration.
These practices, including holistic grazing, agroecological restoration, and community-based farming initiatives, promote the regeneration of degraded land, improve water quality, and contribute to rural livelihoods.
Beyond the Fields: The Socioeconomic Impacts of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture holds immense potential to bring about positive socioeconomic changes at local and global scales.
Below, we examine the broader impacts of sustainable agriculture beyond the agricultural fields themselves.
Empowering Local Communities Through Sustainable Farming Practices
Sustainable agriculture can empower local communities by providing them with access to nutritious food, economic opportunities, and greater control over their food systems.
By promoting diversified farming practices, direct farmer-consumer relationships, and community-supported agriculture, sustainable agriculture strengthens local food networks, reduces dependency on external inputs, and enhances food security.
Enhancing Food Security and Improving Livelihoods

source: https://www.statista.com/chart/21209/best-and-worst-performing-countries-for-food-security/
Food security remains a pressing global concern, particularly in regions vulnerable to climate change and resource constraints.
Sustainable agriculture, with its focus on resilience and diversified production systems, plays a crucial role in ensuring food security.
By embracing sustainable practices, farmers can enhance agricultural productivity, reduce post-harvest losses, and improve the availability of nutritious food, thereby improving livelihoods and reducing poverty.
The Economics of Sustainable Agriculture: Balancing Profitability and Long-Term Sustainability
Sustainable agriculture is often perceived as a trade-off between ecological stewardship and economic viability. However, numerous studies demonstrate that sustainable farming practices can be economically profitable in the long run.
While initial investments and transition periods may pose challenges, sustainable agriculture offers opportunities for cost savings, improved market access, and reduced reliance on expensive external inputs.
Moreover, the environmental benefits associated with sustainable practices can create value through ecosystem services and contribute to long-term economic sustainability.
Embracing the Call to Action
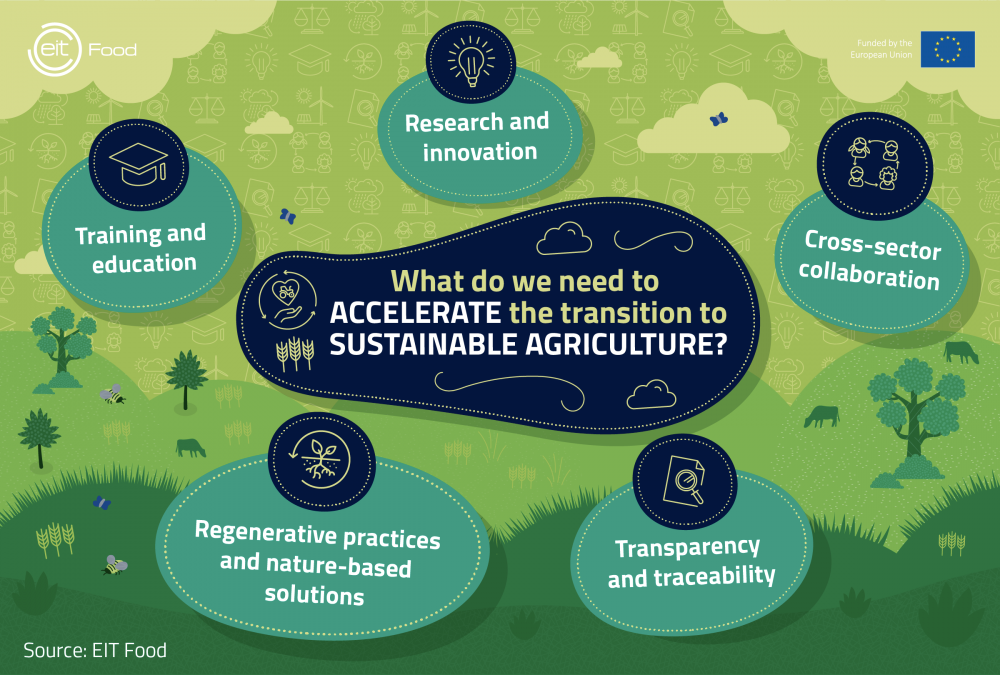
source: https://www.eitfood.eu/blog/5-ways-to-accelerate-the-transition-to-sustainable-agriculture
As the urgency for sustainable agriculture grows, individuals, organizations, and policymakers must collaborate to drive the necessary changes.
Inspiring People to Become Advocates for Sustainable Agriculture
Individuals have a vital role to play in promoting sustainable agriculture.
By making informed choices as consumers, supporting local farmers and sustainable food systems, and advocating for policy changes, everyone can contribute to the wider adoption of sustainable practices.
Education and awareness campaigns play a crucial role in empowering people with the knowledge and tools to become advocates for sustainable agriculture.
Policy and Institutional Support for Promoting Sustainable Farming Practices
Governments and institutions have a significant role in shaping the agricultural landscape.
Policy frameworks that prioritize sustainable agriculture, provide incentives for adopting sustainable practices, and invest in research and development can accelerate the transition toward a more sustainable food system.
Additionally, collaboration between governments, farmers, scientists, and NGOs can facilitate knowledge sharing, capacity-building, and the implementation of sustainable farming practices.
Collaborative Initiatives and Global Efforts Toward a Sustainable Future
Collaborative initiatives at local, regional, and global levels are crucial to advancing sustainable agriculture.
Platforms for sharing best practices, research findings, and innovative solutions can facilitate cross-sectoral collaboration and knowledge exchange.
Global efforts, such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and international agreements on climate change and biodiversity, provide a framework for aligning agricultural practices with broader sustainability objectives.
Conclusion
Sustainable agriculture offers a transformative pathway to meet the challenges of food security, environmental sustainability, and socioeconomic well-being.
By embracing the principles of agroecology, agroforestry, precision farming, and permaculture, we can cultivate resilient farming systems that nourish both people and the planet.
Through sustainable agriculture, we have the opportunity to restore ecosystems, empower local communities, and create a future where our food systems flourish in harmony with nature.
The principles of sustainable agriculture beckon us to join the movement and cultivate a future we can sustain. Let us embark on this journey together, cultivating the future we envision.













No Comments