|
|
In the era of climate change and dwindling natural resources, the way we travel is changing. Traditional gas-guzzlers are gradually being replaced by more eco-friendly alternatives, drawing our attention to the exciting world of solar vehicles and electric cars. As humanity revs up its engines towards a greener future, these innovative modes of transport are becoming crucial pieces in the sustainability puzzle.
Solar vehicles and electric cars are among some of the most promising technological advancements when it comes to sustainability. However, while both offer substantial reductions in carbon emissions compared to conventional vehicles, they differ significantly in their design, operation, and environmental impact.
This article aims to shed more light on these differences and provide a comprehensive comparison between solar vehicles and electric cars. Below, we examine various factors that contribute to their sustainability credentials such as energy efficiency, lifecycle emissions, infrastructure requirements, and overall environmental footprint.
Key Takeaways
- Solar vehicles use sunlight for power, providing unlimited range, but need consistent sunlight.
- Electric cars have no emissions and high energy efficiency but require significant charging infrastructure.
- Solar vehicles have direct energy conversion, electric cars use efficient motors and regenerative braking.
- Both technologies face environmental challenges, including resource-intensive manufacturing and waste management.
- The future of transport likely involves a blend of solar and electric technologies, needing further technological advances.
Solar Vehicles: Harnessing Sunlight on the Go
Solar vehicles are the epitome of sustainable technology, designed to capture and utilize the energy radiated from our sun. According to recent data, the solar-powered car market is growing and is expected to grow by 37% by 2030.
Solar cars are equipped with an array of solar panels, also known as photovoltaic cells, that transform sunlight into electric energy. This energy either propels the vehicle directly or is stored in batteries for subsequent use.
Due to their reliance on strong sunlight for optimal performance, solar vehicles are primarily used in niche areas such as solar races or space rovers. They still remain a novelty rather than an easily available technology.
Nevertheless, the potential for mainstream solar vehicles is increasing with continual advancements in solar technology and battery storage capabilities. These vehicles offer a virtually unlimited range during daylight hours, leading to significant savings on fuel costs while producing zero tailpipe emissions.
The prospect of a vehicle powered entirely by renewable energy is enticing and positions solar vehicles as a truly environmentally friendly mode of transport.

Electric Cars: A Leap from Fuel to Grid
Electric cars have already created a significant shift in the transportation landscape. One in seven cars sold globally now is electric, and in 2022 alone, there were 10.6 million electric vehicle sales globally. And for a good reason — these vehicles operate on rechargeable batteries that can be powered up at home or at dedicated charging stations.
Although the source of this electricity may still come from non-renewable energy, electric cars produce no direct exhaust emissions and exhibit superior energy efficiency compared to their conventional gasoline-powered counterparts.
As nations across the globe progressively lean towards cleaner methods of electricity production, the carbon footprint of electric cars is poised to reduce even further. Combined with their increasingly affordable price tags and improved range capacities, electric cars are becoming practical and sustainable substitutes for traditional fuel-based vehicles.
Energy Efficiency Showdown: Solar vs. Electric
When it comes to energy efficiency, both solar vehicles and electric cars have much to offer, outpacing their traditional gasoline-powered counterparts by a considerable margin. However, how they achieve this efficiency is quite different.
As mentioned before, solar vehicles utilize the sun’s energy directly through photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. This electricity then powers the vehicle’s motor or is stored in a battery for later use.
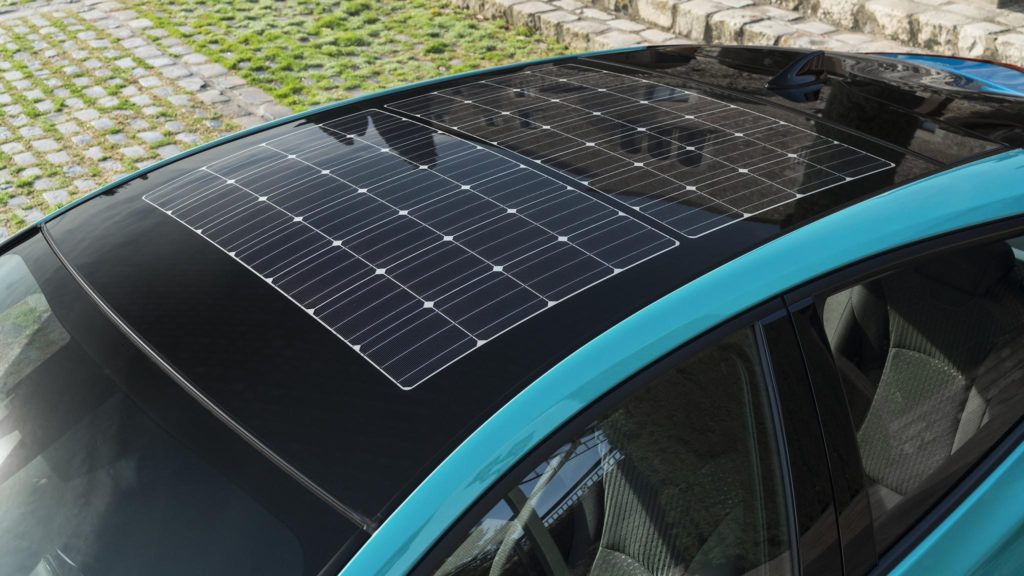

Image source. A solar roof on Toyota Prius.
This direct conversion process allows solar vehicles to achieve extraordinary energy efficiency rates as there is minimal energy loss during the conversion. Moreover, the fuel for solar vehicles — sunlight — is not only free but also endlessly renewable, adding another layer of efficiency.
Electric cars, on the other hand, are powered by electricity that has been generated elsewhere and stored in high-capacity batteries. Despite this indirect process, electric cars are still highly energy-efficient.
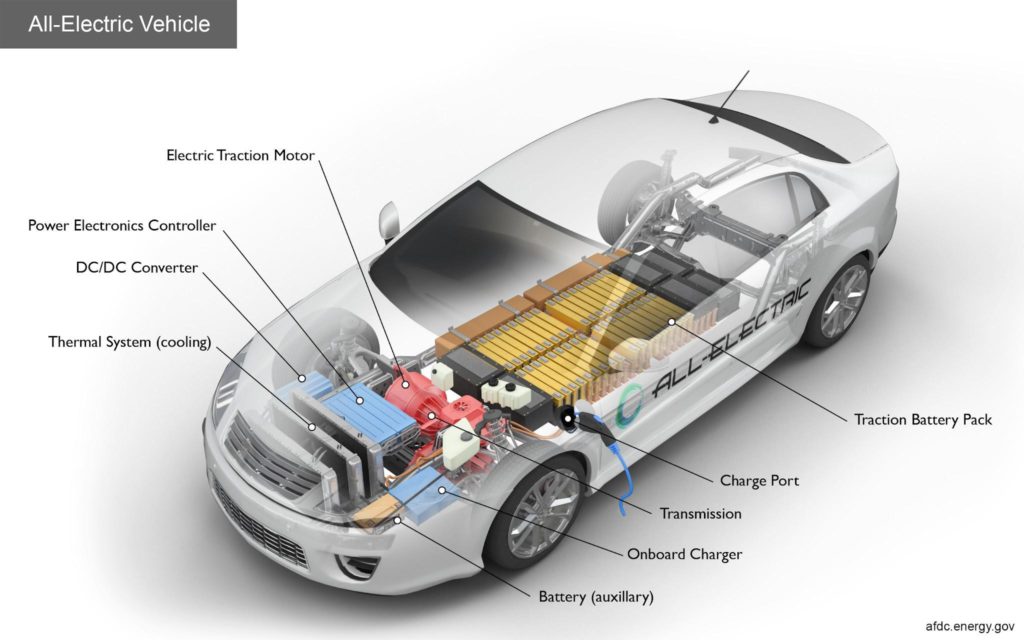
Image source. Key components of an all-electric car.
For starters, electric motors are inherently more efficient than internal combustion engines due to fewer moving parts and the ability to convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into drive power. Additionally, electric cars can also recover and store energy during braking, a feature known as regenerative braking, which further enhances their overall efficiency.
So, who wins the showdown?
It’s challenging to declare an outright victor as both have their strengths and weaknesses. Solar vehicles can achieve higher efficiency rates due to direct energy conversion but are reliant on consistent sunlight exposure. Electric cars can operate efficiently in a wider range of conditions but depend on external sources of electricity, which may not always be derived from renewable sources.
The real takeaway here is that both solar and electric vehicles represent enormous strides toward more energy-efficient transportation. As technology continues to evolve and renewable electricity generation becomes more widespread, these vehicles will play key roles in the world’s slow but gradual transition to more sustainable mobility.
Infrastructure Requirements: A Key Consideration for Sustainability
Infrastructure plays a crucial role in the sustainability narrative of both solar vehicles and electric cars. Each requires distinct infrastructural support, the development of which can have significant implications for their widespread adoption and long-term environmental impact.
Solar vehicles are relatively low-demand when it comes to infrastructure. They primarily rely on the sun, requiring no specific charging stations or power outlets. However, they do need a clear and consistent source of sunlight, making them less viable in areas with frequent cloud cover or limited daylight hours.
Moreover, given that solar vehicles are still largely in the experimental stage, there may also be a need for specialized maintenance and repair facilities that could add to the infrastructure requirements.
Conversely, electric cars require a powerful network of charging stations to ensure usability and convenience for users. This is especially important for long-distance travel where recharging would be necessary. The development of this charging infrastructure poses both challenges and opportunities.
On the one hand, building new infrastructure requires significant energy and resources. On the other hand, it presents an opportunity to further integrate renewable energy into our daily lives as these charging stations could be powered by green energy sources.
Environmental Footprint: Beyond Carbon Emissions
In assessing the environmental footprint of solar vehicles and electric cars, it’s crucial to look beyond carbon emissions to encompass a broader range of impacts. These include elements such as water usage, air pollution, waste generation, and resource extraction.
Solar vehicles, for instance, depend on solar panels, which require significant amounts of water and energy to produce. The manufacturing process can also generate hazardous waste if not managed properly. However, once operational, these vehicles produce almost no pollution, and their fuel — sunlight — requires no extraction or transportation.
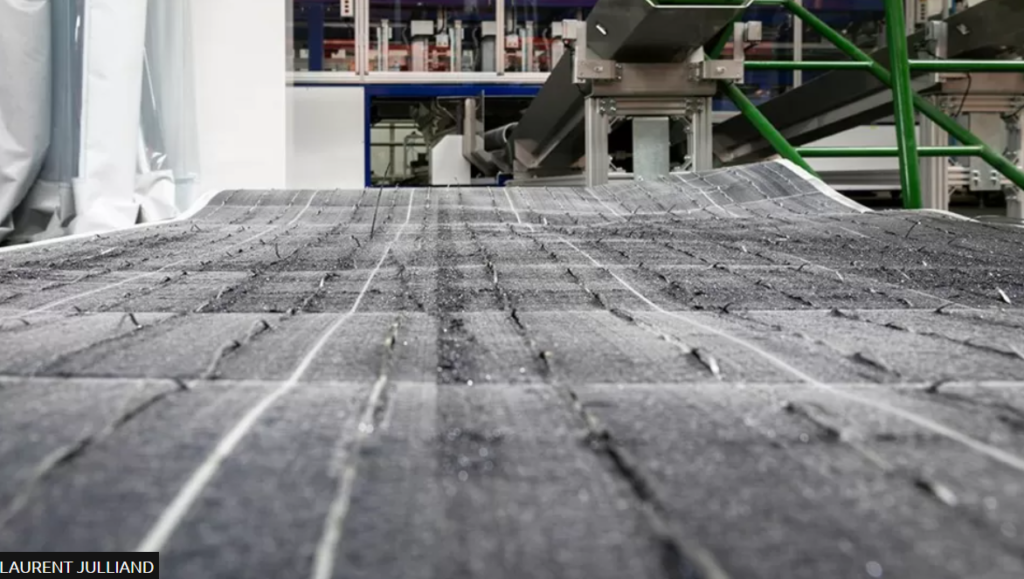
Image source. Solar panels can be delaminated in order to recover precious materials and minimize waste that goes into landfills.
Electric cars also bring unique environmental considerations. While they produce zero tailpipe emissions, the production of their batteries is resource-intensive and can lead to harmful environmental impacts.
The mining activities necessary to extract lithium, cobalt, and other rare metals for battery production can result in habitat destruction, soil contamination, and water pollution if not carefully controlled. Plus, at the end of their life cycle, handling and disposing of these batteries present additional environmental challenges.
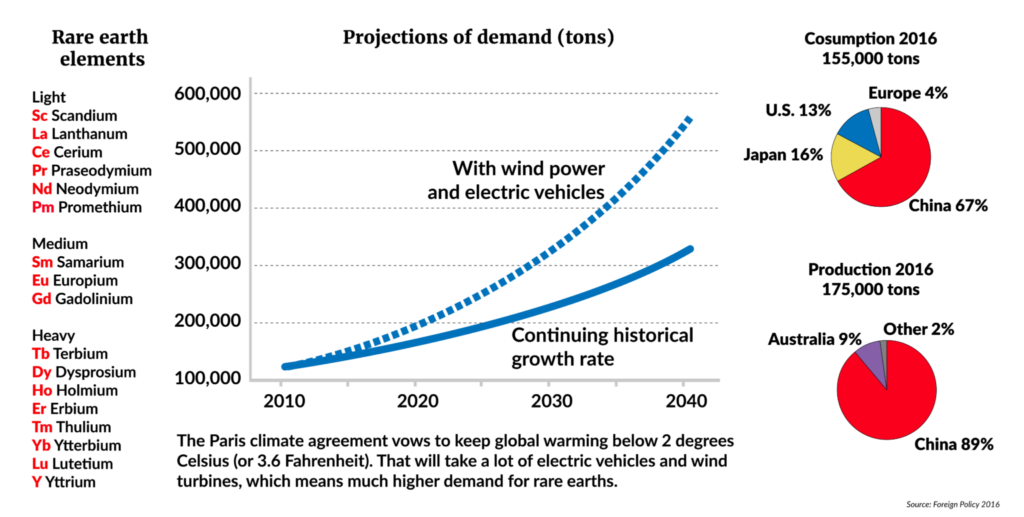
Image source. A graph showing how the energy revolution can be stunted by raw material shortages.
However, it’s worth noting that efforts are underway to mitigate these impacts. Improvements in production efficiency for both solar panels and batteries can reduce water and energy use. Recycling programs can also help manage waste and decrease the need for new resource extraction.
Ultimately, while both solar vehicles and electric cars have environmental footprints that extend beyond carbon emissions, they still represent a significant improvement over traditional internal combustion vehicles.
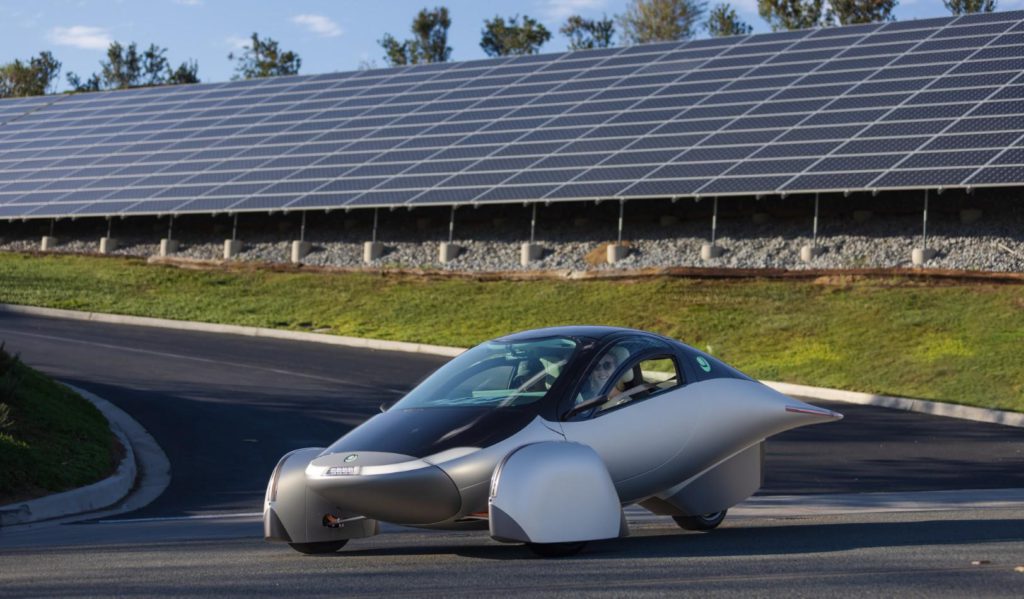

Image source. The innovative design of a solar-powered vehicle by Aptera Motors.
Pioneers of Sun-Driven Mobility
Companies like Aptera Motors and Lightyear are currently at the forefront of this solar revolution.
Aptera Motors has developed a highly aerodynamic, three-wheeled electric vehicle equipped with built-in solar panels that can travel up to 40 miles a day solely on solar power. Meanwhile, Lightyear is working on a luxury electric vehicle that can cover an impressive range using its integrated solar cells.
These pioneering companies, along with numerous researchers and engineers worldwide, are overcoming significant technical challenges to make solar vehicles a viable option for everyday use. Their tireless work is driving us towards a future where our vehicles run on clean, renewable energy directly sourced from the sun.

Image source. 2023 Tesla Model S.
The Stars of the Electric Revolution
In parallel with these advancements in solar technology, other innovators are leading the charge in the electric revolution. These leaders are proving that vehicles powered by electricity can be just as reliable, practical, and exciting as traditional internal combustion engine cars — all while significantly reducing environmental impact.
Tesla is undoubtedly one of the shining stars in this sphere. Under Elon Musk’s leadership, Tesla has demonstrated that electric cars can offer top-tier performance, long-range capabilities, and high-tech features that captivate consumers.
Other major manufacturers like Nissan with their Leaf model and Chevrolet with their Bolt EV have also made significant strides in making electric cars more accessible to everyday drivers.
Furthermore, newer players like Rivian and Lucid Motors are entering the market with their own innovative electric models. Rivian focuses on creating rugged electric adventure vehicles, while Lucid Motors aims to redefine luxury in the electric vehicle market.
These companies represent just a fraction of the ongoing innovation in the electric vehicle industry. With each technological breakthrough and new model released, they’re driving us closer to an electrified future where sustainable transportation is not just possible but preferable.
Final Thoughts
As we navigate towards a greener future, both solar-powered vehicles and electric cars will play pivotal roles in revolutionizing our transportation systems. However, each technology comes with its unique set of challenges and benefits.
For solar-powered vehicles to become mainstream, enhancements in photovoltaic efficiency and energy storage capacity are required to overcome limitations imposed by inconsistent sunlight availability.
For electric cars to achieve mass adoption, continued investment in charging infrastructure combined with advances in battery technology will be key catalysts. Additionally, shifting electricity generation towards more sustainable sources will greatly reduce their lifecycle emissions.
Ultimately though, it’s likely that a combination of technologies — potentially even hybrids of solar and electric — that will steer us away from our current reliance on fossil fuel-powered automobiles.












