|
|
Natural gas, an invaluable non-renewable fossil fuel, has a rich and ancient history that spans hundreds of millions of years. It started when tiny sea creatures, plants, and animals passed away, and their leftovers turned into the energy we use today. This amazing change happened a very long time ago, about 300-400 million years ago, and it created the energy we rely on in our world today.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in renewable energy sources, and natural gas has often been considered one of them. In this article, we will explore the concept of natural gas as a renewable energy source and address some commonly asked questions.
The Nature of Natural Gas
Natural gas, composed mainly of methane (CH4), is a naturally occurring fossil fuel beneath the Earth’s surface. This energy source results from millions of years of geological processes acting on the remains of ancient plants and animals.
These organic materials, buried deep underground, transform due to the immense heat and pressure of the Earth’s crust, converting into the hydrocarbon-rich substance we know as natural gas.
Geological surveys and exploration efforts are essential for pinpointing natural gas reserves. Once identified, drilling wells, whether onshore or offshore, depending on the reserve’s location, become the conduits to access these underground reservoirs.
The utilization of advanced drilling technologies ensures the safe extraction of this valuable resource playing a crucial role in the broader world of diesel and petroleum production.
Natural Gas: Renewable or Non-Renewable?

The classification of natural gas as either renewable or nonrenewable has been the subject of ongoing debate within the energy and environmental sectors. While natural gas is fundamentally a fossil fuel, traditionally considered nonrenewable because it is finite and formed over geological time scales, there is an emerging argument that certain forms of natural gas can be regarded as renewable.
Natural gas is often referred to as a renewable energy source due to the significant potential for renewable natural gas (RNG) production. RNG is produced from organic waste materials, such as agricultural waste, landfill gas, and wastewater treatment plants.
These waste materials contain methane, which can be captured and processed into RNG. Since the production of RNG relies on continuously available waste streams, it can be considered a renewable source of natural gas.
Examples of Renewable Natural Gas (RNG)
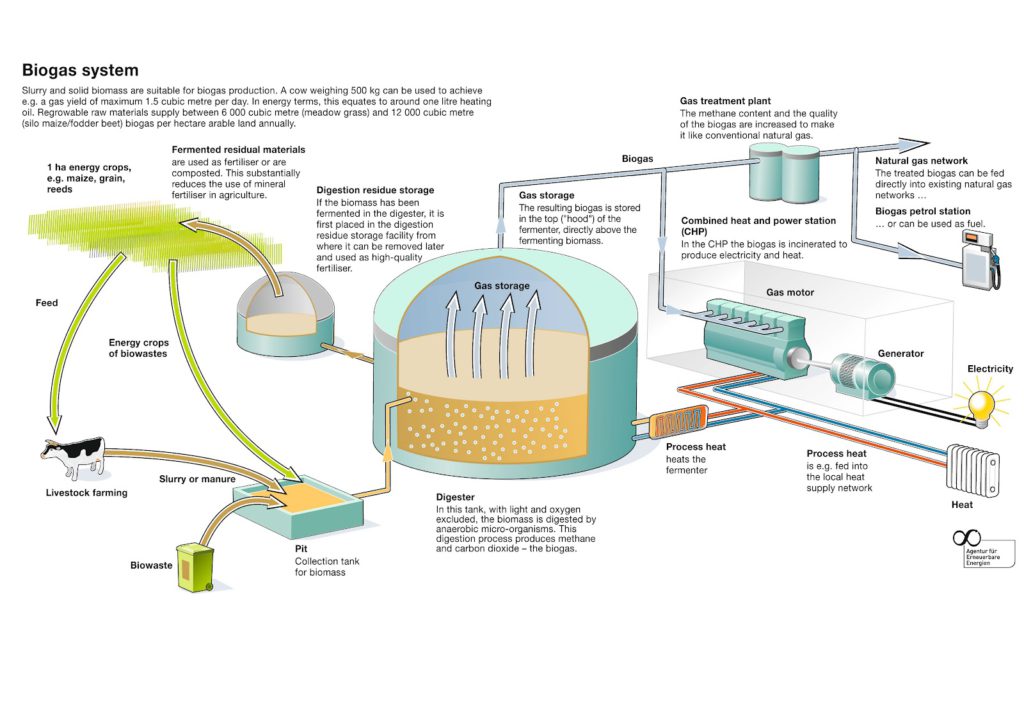
Image Credit: en-planet-biogas.net
1. Biogas: A good example of renewable natural gas is biogas. It comes from breaking down waste in landfills, sewage plants, farms, and kitchen scraps. Biogas is mostly made of methane, like regular natural gas, but it’s made from trash, not fossil fuels. This helps stop methane pollution in the air, which is better for the environment.

Image Credit: Braduk.net
2. Hydrogen-Rich Gas: Another emerging development is producing hydrogen-rich gas from renewable energy sources like wind and solar power. Through electrolysis, water is split into hydrogen and oxygen, and the resulting hydrogen gas can be combined with carbon dioxide to produce synthetic natural gas (SNG). SNG has the potential to be carbon-neutral when produced using renewable electricity and carbon capture technologies.
Providing hydrogen to industries is now a big global business. The need for hydrogen has grown three times since 1975 and keeps increasing. Most come from fossil fuels, with 6% from natural gas and 2% from coal.
However, making hydrogen this way creates a lot of CO2, about 830 million tons early. That’s like the CO2 emissions of both the United Kingdom and Indonesia combined.
Production of Natural Gas
Natural gas, a valuable energy source, is obtained by drilling wells and extracting it from underground reservoirs. This process begins with drilling wells deep into the Earth’s crust to reach these underground reservoirs where natural gas is trapped.
Examples of Natural Gas Production
- Exploration Drilling: Exploration drilling involves identifying potential natural gas reserves. Advanced technologies, such as seismic surveys and geological analysis, help geologists and engineers locate areas with high natural gas potential.
- Extraction: Once a suitable site is identified, production wells are drilled. These wells penetrate deep into the Earth’s layers to reach the natural gas reservoirs. Various techniques, including hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and conventional drilling, are used depending on the geological conditions.
Processing and Purification
After being extracted, natural gas is transported to processing plants via pipelines. At these processing facilities, the raw natural gas undergoes purification to remove impurities that can be harmful or undesirable:
- Water Removal: Water vapor in the raw gas is removed, as excessive moisture can cause corrosion in pipelines and equipment.
- Hydrogen Sulfide Removal: Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a toxic and corrosive gas, is eliminated to make the gas safer and to prevent damage to pipelines and equipment.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: Carbon dioxide (CO2) is another impurity removed from natural gas to improve quality and prevent environmental emissions.
Distribution and End Uses

Image Credit: The Sportsman’s Guide
Once purified, natural gas is transported via an extensive network of pipelines to homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. It serves a multitude of purposes, including:
- Electricity Generation: Natural gas power plants are a major source of electricity in many countries due to the fuel’s efficiency and relatively low emissions.
- Heating: Natural gas is commonly used for heating residential and commercial spaces. It is particularly popular for its convenience and cost-effectiveness.
- Industrial Applications: Various industries utilize natural gas as an energy source for processes such as manufacturing and refining.
Role of Natural Gas in the Energy Transition
Natural gas is pivotal in our journey towards a cleaner and more sustainable energy landscape. Here’s a breakdown of its significance:
Why Natural Gas Matters
- A Greener Option: Regarding environmental impact, natural gas is a cleaner choice than its dirtier counterparts, like coal and oil. It doesn’t release as many harmful pollutants and particulates into the atmosphere.
- A Transition Fuel: Think of natural gas as a vital link between our old, polluting energy sources and the cleaner energy solutions of the future. It’s like a bridge helping us transition from less eco-friendly options to cleaner alternatives.
Concrete Examples
- Reduced Pollution: Using natural gas instead of coal to generate electricity significantly reduces air pollution. This means clearer skies, healthier air, and a better environment.
- Less Climate Impact: Natural gas emits fewer greenhouse gases than coal and oil, the culprit behind climate change. Choosing natural gas helps in the fight against global warming.
Role of Natural Gas in the Energy Sector

Natural gas is a big deal in the alternative energy companies because there’s a lot of it, and it can do many things. Think of it like a superhero of energy! It helps make electricity, keeps us warm in our homes, and even cooks our food in our kitchens. Natural gas power plants are like the strong and steady heroes in our energy world, ensuring reliable electricity.
We also find natural gas in our houses, making sure our heaters work well and our stoves can cook delicious meals. But natural gas doesn’t stop there; it’s like the secret ingredient in many things we use daily. It helps make chemicals and plays a part in creating all sorts of stuff we need, like the materials for building cars and making everyday items.
So, when we talk about our energy future, natural gas is like a valuable friend, helping us in many ways. But remember, there are also other heroes in the energy world, like renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power.
They’re like the new kids on the block, helping us move towards a cleaner and greener energy future. Using natural gas wisely and exploring cleaner alternatives is important to create a better tomorrow for our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Natural gas is a fossil fuel and a renewable energy source formed from the remains of plant and animal materials buried and subjected to heat and pressure over millions of years.
No, natural gas is not considered renewable. It is a fossil fuel formed from the decomposition of organic matter over millions of years and is, therefore, a nonrenewable energy source.
Natural gas is often called a renewable energy source because it produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions than other fossil fuels like coal or oil. However, it is important to note that natural gas is not renewable.
Natural gas is produced by drilling and extracting natural gas deposits found deep underground. extracted, it is processed and transported through pipelines or stored for later use.
Natural gas plays a significant role in the energy transition as it can be a cleaner alternative to other fossil fuels. It can generate electricity, heat buildings, and power various industrial processes.
Natural gas is often considered a cleaner energy source than coal or oil because it emits less carbon dioxide and other pollutants when burned. However, it still produces greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Renewable natural gas, or biogas, is natural gas produced from organic waste materials such as agricultural waste, landfill gas, or wastewater treatment plants. It is considered renewable because it is produced from sustainable and renewable sources.
Natural gas is primarily composed of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Although natural gas combustion produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions than other fossil fuels, methane leakage during production, transportation, and distribution can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Natural gas is critical in the energy sector as it is used for electricity generation, heating, and as a fuel for various industrial processes. It is also used as a feedstock to produce hydrogen and other chemicals.
Natural gas is used for energy by burning or combusted in power plants or furnaces to generate heat or electricity. It can also be used in vehicles as a fuel or converted into other forms of energy, such as hydrogen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding natural gas reveals its pivotal role as a versatile and abundant energy source. It has powered our homes, industries, and daily lives for decades. However, as we look to the future, we must recognize the importance of balancing its benefits with the imperative of sustainability.
While natural gas contributes significantly to our energy mix, embracing renewable sources alongside it is essential for a cleaner, more environmentally friendly energy landscape. Doing so can ensure a brighter and more sustainable future for generations to come.












