|
|
Get ready for an exciting journey into the world of animal habitats! We’re diving deep into what habitats are and why they’re super important for animals. As you flip through this article, you’ll discover how animals like habitat experts, adapt to their special homes.
Imagine going through different habitats like forests, oceans, and more. You’ll also consider what happens when habitats are destroyed and how animals pick their homes. Get ready to be amazed by the incredible lives of animals and how they fit into their changing habitats.
What is a Habitat and Why is it Important for Animals?
Imagine a habitat as a crucial puzzle piece in an animal’s life – it’s like their home and lifeline. This natural dwelling is where animals live and thrive. Picture it as a nurturing space, like a cozy home, where animals can find everything they need to stay alive and healthy. These things include food, water, safe places to rest, and special spots for them to have babies and raise their little ones.
Habitats are like the stages where animals play their roles in the big show of life. Think of each habitat as a unique theater with its own set – the climate, plants, and geography. As actors perform different parts in a play, animals fit into their habitats based on their special features.
Over time, animals change and adapt to match their habitats, almost like they’re creating different costumes and learning new scripts. This helps them fit in and survive in their homes, shaping how they live, interact, and survive together in the intricate story of Earth’s life.
Here are some of the essential facts about habitats you should know:
1. How Different Animals Adapt to Their Specific Habitats

The natural world showcases remarkable adaptations that animals have developed to conquer the unique challenges of their specific habitats. From soaring skies to deep oceans, creatures have undergone remarkable changes to ensure survival.
For instance, aquatic animals that call water home have undergone fascinating transformations. Their streamlined bodies and specially designed webbed feet enable them to glide seamlessly through the water, mastering their liquid environment.
A study by Lauder (2006) illustrates how aquatic animals’ body shapes and fin structures are perfectly engineered for efficient swimming, demonstrating how adaptation leads to mastery in their watery abode.
On the other hand, animals that brave the arid landscapes of deserts exhibit remarkable strategies to endure the harsh conditions. These creatures have evolved water-conserving mechanisms and efficient heat-regulation techniques.
For instance, the kangaroo rat, a desert dweller, extracts water from its food and has concentrated urine to minimize water loss. Also, kangaroo rats possess remarkable adaptations that facilitate their ability to detect and evade predators with remarkable efficiency. Featuring robust hind legs, these rats can execute leaps spanning up to nine feet in a single bound, enabling swift evasion from agile and stealthy predators.
These remarkable strategies enable desert animals to survive and thrive in habitats with scarce resources and extreme conditions.
2. Terrestrial Habitats: A Multitude of Landscapes and Adaptations

Terrestrial habitats are like a bustling neighborhood for animals, with each environment having its unique set of residents who have become masters of survival in their surroundings.
Forests are like the ultimate hideout for animals, offering them shelter and a buffet of delicious treats. It’s like a big family reunion, where creatures team up to make life comfy for each other. Scientists at the World Wildlife Fund have been like habitat detectives, studying the relationships in forest communities to understand their secret code.
Also, deserts are the ultimate animal challenge, like a survival reality show. In this arid desert world, life has become a master of saving water and developing cool tricks to stay hydrated. Desert animals have cleverly adapted to their tough environment, using tricks to stay cool and save water.
For example, camels can go weeks without water and have special nostrils and eyelashes to keep sand out. Creatures like the fennec fox are active at night, coming out to hunt when the sun is gone. Others, like the desert tortoise, prefer living underground. Desert birds move around to find food, and the Namib desert beetle collects water from fog. These amazing changes make desert animals easily affected by changes in their homes, making them more vulnerable to shifts.
3. Aquatic Realms: An Abundance of Life Below the Surface

Water habitats, like lakes, rivers, oceans, and coral reefs, hold incredible mysteries. Some places, like lakes and rivers, are calm, while others, like the deep ocean and colorful coral reefs, are full of secrets.
Aquatic habitats host an incredible variety of life, from the tiniest microorganisms to the largest marine creatures. The Census of Marine Life, a comprehensive global research initiative, revealed that over 230,000 known marine species have been documented, with countless more yet to be discovered.
Over 6,000 potential new ocean species were found by about 2,700 scientists from 80+ countries during the Census of Marine Life decade. They explored oceans worldwide, from the chilly poles to the sunny tropics, studying creatures from large whales to tiny microbes. They also examined fish movements and historical records to understand the ocean’s past before human impact and used this knowledge to ponder its future.
Another interesting fact is that coral reefs in marine aquatic habitats are home to a quarter of all marine species despite covering just 0.1% of the ocean’s surface. The coral reefs of the Northwest Hawaiian Islands in the Papahānaumokuākea National Marine Monument showcase the rich life found in shallow-water reef ecosystems. These reefs are home to over 7,000 species, including fishes, plants, sea turtles, invertebrates, birds, and marine mammals.
4. Aerial Habitats: Aerial Mastery and Survival Strategies
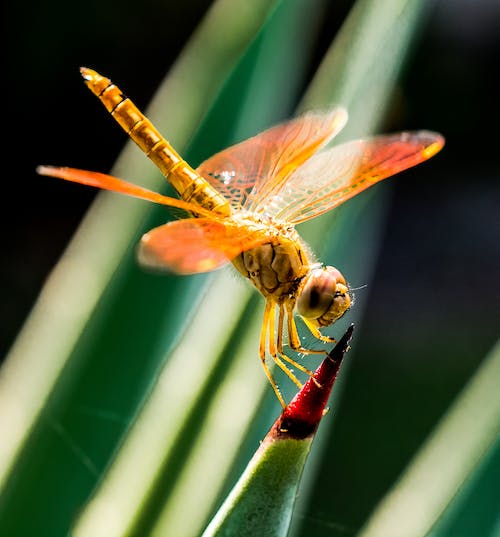

Discover the captivating realm of aerial habitats, where the art of flight becomes a remarkable survival tactic. Birds and bats showcase the wonders of adaptation as they effortlessly navigate the skies.
Research into avian flight mechanics uncovers the intricate dance of aerodynamics and physiological tweaks that empower birds to dominate the air. These adaptations highlight the harmony between animals and their environment, offering a peek into the enchanting complexities of the natural world.
Yet, the aerial world isn’t exclusive to birds and bats alone. Insects, including dragonflies have also embraced this domain. Marine biologist Charles Anderson observed groups of globe skimmer dragonflies landing in the Maldives during autumn before embarking on a journey to East Africa.
This led to an intriguing revelation in 2009: these migratory dragonflies, measuring just five centimeters, remarkably traverse the Indian Ocean, flying seasonally from India to East Africa and back. This feat, potentially facilitated by high-altitude winds, marks the world’s longest non-stop migration by such a small creature, surpassing even the famous North American Monarch butterflies.
5. How Habitat Destruction Impacts Animal Populations

How people change the environment, like cutting down trees, building cities, making things dirty, and using more land for farming, greatly affects where animals live. This cannot be good for animals. When their homes get destroyed or broken into smaller pieces, it messes up their neighborhoods and makes many animals leave.
Recently, several examples of animal habitat destruction have been caused by human activities. One such instance is the Amazon rainforest, often called the “lungs of the Earth,” which has been facing deforestation due to logging, mining, and agriculture. This habitat loss threatens the diverse range of species that call the rainforest home, including jaguars, sloths, and bird species.
Another example is the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, which has been impacted by coral bleaching caused by rising ocean temperatures due to climate change. Coral bleaching occurs when the colorful coral reefs turn white and lose their ability to support marine life. This directly affects the fish, turtles, and other creatures that rely on the reef for shelter and food.
6. Animals Cannot Adapt to Climate Change
Climate change profoundly affects animal habitats, disrupting ecosystems and posing significant challenges for various species. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and vegetation shifts directly impact animals’ ability to find food, shelter, and suitable breeding conditions. Here are a few examples:
- Polar Bear Habitat Loss: The warming Arctic due to climate change is causing sea ice loss, which is crucial for polar bears to hunt seals, their primary food source. As the ice melts earlier in the spring and forms later in the fall, polar bears have less time to hunt and build up the fat reserves they need to survive during the ice-free months on land. Watch here the penguins in the Antartic from BBC Earth.
- Migration Patterns: Many animals rely on specific cues, such as temperature changes and food availability, to time their migrations. However, with shifting climate patterns, these cues are disrupted, affecting the timing of migrations. For example, some bird species arrive at their breeding grounds before their insect prey emerges, impacting their ability to find food for their young. Discover in a Youtube video how climate patterns thousands of miles away affect US bird migration.
- Altered Forest Habitats: Warmer temperatures can change forest composition and structure, affecting animals that depend on specific tree species for food and shelter. For instance, as temperatures rise, some tree species may shift their range to higher elevations, impacting animals that rely on them.
These examples highlight the far-reaching impacts of climate change on animal habitats, emphasizing the urgent need for global efforts to mitigate its effects and safeguard the future of Earth’s diverse species.
Frequently Asked Questions
Animals can be found in various habitats, such as forests, deserts, oceans, grasslands, and wetlands.
Animals are adapted to survive in their specific habitat. Living in their natural environment allows them to find shelter, obtain food, and reproduce successfully.
Animals have different ways of finding food depending on their species. Some animals hunt and capture prey, while others graze on vegetation or scavenge for food.
Yes, animals need a specific environment with the necessary resources such as food, water, shelter, and suitable climate conditions.
Some animals are more adaptable and can survive in various habitats, while others are specialized and can only live in specific environments.
Animals may sometimes move from one habitat to another depending on factors such as availability of food, mating opportunities, or changes in weather conditions.
Animals have different fur colors as a result of natural selection. The color of their fur helps them blend into their surroundings and provides protection from predators.
The state of the environment can have a significant impact on animals. Changes in habitat due to human activities, pollution, or climate change can disrupt food chains and threaten the survival of certain species.
Yes, animals play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the environment. They help control the population of other organisms, disperse seeds, and contribute to the overall health of ecosystems.
People can help keep animal habitats intact by supporting conservation efforts, reducing pollution, preserving natural areas, and promoting sustainable practices.
Conclusion
In the grand tapestry of our planet’s ecosystems, the role of conservation stands as a vital thread woven with purpose and passion. As we conclude this exploration into the intricate realms of animal habitats, it becomes abundantly clear that the pursuit of conservation is not merely an option but a necessity.
A symphony of efforts orchestrated by conservation organizations resonates to establish havens of protection, harmonize with sustainable land practices, and illuminate the profound significance of preserving the natural world.
These endeavors ripple beyond the borders of habitats and species, extending to the fabric of our shared existence. Conservation ensures that the intricate dance of life continues, from the smallest creatures to humanity itself. By safeguarding habitats, we embrace a future where the symphony of nature remains harmonious, animals thrive, and the delicate balance of our interconnected world perseveres for generations to come.