|
|
The scoop: Web 3 is not 100% virtual. The sustainability of Web 3 depends on energy that derives from the physical world. Still, the next evolution of the Internet has the potential to influence sustainability around the world.
Key points:
- Only about 12% of the energy in the US comes from renewables.
- Web 3 applications can offset energy consumption by making other aspects of our economy more sustainable.
- It’s still early. We are likely to see unexpected solutions come from unexpected areas. Buckle up for the ride.
What’s next? Rather than predicting the future, we can spot existing trends that will influence the development of sustainability in Web 3 over time.
Dig deeper → 5 min
As we all know, the web lives in a virtual space. But it is tethered to the physical world by the energy needed to power it.
This massive energy requirement will ultimately determine its sustainability. We must also factor in, however, the impact of how Web 3 will change the way we operate.
Before delving into the potential environmental impact of Web 3 long-term, it’s helpful to set some context.
What Web 3 Really Is (and Is Not)
Web 3 is a bottom-up evolution of the internet that prioritizes decentralized, distributed services over centralized ones.
This isn’t a Google or Facebook invention arriving on our phones next spring.
Rather, Web 3 is spread out and pieced together through a complex web of varying entities all over world, ranging from individual entrepreneurs to large development communities (called DAOs).
Anyone with internet access can launch a web3 project and communicate with other web3 projects.

You may find it helpful to think of Web 3 as a collection of applications that utilize new technologies rather than a single new operating system. Web 3 apps provide a significantly different functionality to the internet than what we are used to in the current web (Web 2.0).
By “connecting your wallet”, you are bringing your digital property along with you to a new arena. When you are done playing on a platform, you can pick up, leave, and bring your digital assets somewhere else.
How Do We Know What A Web 3 Application Is?
Whether you know it or not, you’ve probably already participated in Web 3. Or at least used an application made possible by it.
Web 3 technologies are characterized primarily by these concepts:
- Decentralization – moving away from central websites and services like Google, Facebook, and Amazon that own and manage your data; moving toward sites run by a community and all users controlling their own data.
- Governance – moving away from gatekeepers who currently decide who and how you can access resources on the web; moving toward free access and unbridled participation.
- Privacy – moving away from data collected and owned by a corporation; moving toward owning and managing your own data.
The world is transitioning away from an internet dominated by large companies that control the flow of information (think Facebook hosting and controlling your data).
Instead, we are committed to open platforms that enable individuals to own their data. You can learn more about Web 3 social networks here, as explained by Ethereum, one of the largest Web 3 innovators.
The underlying technology that enables our transition toward autonomy and control over our data is the blockchain. This is where the link between the internet and energy usage collide and where we make or break how sustainable Web 3 applications are.
How sustainable will this new collection of Web 3 applications be?
Web 3.0 and Sustainability
It is difficult to predict how Web 3 will evolve its energy use.
Still, there are a few existing trends that could make or break the sustainability of Web 3.
Updating The Foundation
Encryption is one of the underlying foundations of Web 3 tech.
It helps secure the flow of information and ownership of digital assets without requiring middlemen. For almost all blockchains, the process of encrypting information takes up computational power which is energy intensive.
You’ve likely already heard facts around how energy intensive Bitcoin mining is.
Essentially, to securely store information to the blockchain requires energy. Right now, like all other human activities that require energy, most of this energy is coming from fossil fuels.
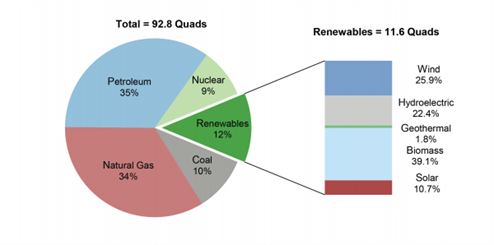
At our current rate, the proliferation of blockchain technologies is outpacing our world’s transition to renewable energy.
There are multiple web3 projects a focus on renewable energy, developing less energy-intensive methods for securing their blockchains. Monitoring improvements in energy efficiency in line with the world’s broader move toward more renewable energy is a key indicator for Web 3 sustainability.
Efficiency in Unexpected Areas
Newer blockchains are focusing on energy efficiency and the development communities of the foundational blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are also actively working on upgrades to decrease the energy intensity.
However, there’s aspect rarely mentioned in the debate over blockchain and sustainability.
Some Web 3 applications provide radical new ways for people and companies to become more sustainable. While the blockchain itself may not be carbon neutral, what this technology enables others to do can help reduce the world’s carbon footprint in other ways.
One example: the carbon offset trading market.
The high cost and difficulty of trading carbon credits to offset emissions has excluded small companies and individuals from participating.
Now, projects create utility assets like Digital Carbon Credit Coins to allow anyone to access carbon trading markets. This is an area previously reserved for governments and large corporations.
There is an unprecedented demand for solving environmental challenges. This opens the doors for new innovation, and smart minds are working together through web3 to reduce to spark new possibilities.
Transparency to Enable More Bottom Up Pressure for Change
While the 2019 global pandemic temporarily decreased consumer-driven pollution, clearing the skies in some major cities around the world, the most recent market trends show that previous gains in ethical compliance have actually regressed. What’s going on?
For those who value the environment and the quality of life, the core problem is:
- We are consuming resources at a faster pace than what the world can sustain
- Our focus on the monetary price of products incentivizes unethical production methods in an effort to be competitive
This is arguably the most foundational problem we face in regards to the sustainability of our environment and society.
While most consumers say they support environmentally friendly and ethically derived products, product lifecycle information is dismally opaque.
A few consumer empowerment apps try to increase transparency, but they’ve barely scratched the surface on making responsible purchases. Companies share very little about their product lifecycle.
As a result, those seeking conscious consumerism often find the burden of responsible shopping too exhausting.
If we stored a product’s life history on the blockchain, however, anyone could see its materials. We could also learn about its origins, and calculate its carbon footprint. This liberates consumers to make a judgement on the environmental and ethical costs of a product.
How would knowing the actual footprint of a product change your buying habits?
A Few Final Considerations
For the Web 3 optimist there’s one final game changer to look forward to. The blockchain tech propping up Web 3 creates an environment ripe for innovation:
- Data becomes more accessible
- Open source programs lower the barrier to entry for developers
- Compensation becomes more direct via cryptocurrencies
These conditions encourage anyone and everyone to participate and be rewarded for it. Anyone with a smart device and internet access can launch a Web 3 app that offers a solution.
They’ll be credited for their work, as it’s stored on the blockchain, and they can be paid for their valuable solution through cryptocurrencies which require no brokers.
Just like evolution in nature, we need a large number of experiments, allowing the top few winners to excel, then iterate again and again. Over time we’ll find unexpected solutions to many of our most pressing problems.












No Comments