|
|
The effects of climate change are already here. How have rising ocean temperatures impacted the supply chain, and what does the future hold?
Busy? Try the speed read.
The scoop: Supply chains must respond to increasing demand for climate action.
Key talking points:
- People can see the potential effects of climate change in places like the Rhine River in Europe and Texas with its winter energy crisis.
- Rising ocean temperatures are pushing lobsters north and making it harder for these creatures to reproduce, harming the seafood industry in the Northeast.
- In response to consumers and investors, automakers are transitioning to electric vehicles, even for the most popular models.
- The effects will worsen if governments and the private sector don’t act quickly. Droughts, wildfires, hurricanes, and other storms will get stronger and cause further damage to industries, the environment, and the supply chain.
Dig deeper → 5 min
Climate change has started to rear its ugly head. The weather has become more volatile in the past few years with dangerous hurricanes, frequent tornadoes, and devastating floods. People have lost their homes, loved ones, and jobs because of global warming. Now, paired with the pandemic, climate change has expedited issues.
What industries have global warming affected? How will rising ocean temperatures affect the supply chain in the long term?
How has climate change affected global supply chains?
The world has become much more interconnected. Countries depend on each other for supplies, thus creating a chain that links everybody. Over time, companies have made their processes more efficient, leading to a greater output of supplies, higher profits, and lower prices for consumers. However, climate change slows progress and even reverses course.
Scientists have been warning about climate change for decades. Since the 1970s, experts have written about climate change and how it has already started to affect the world. The United States and other United Nations (UN) members discussed global warming during the Cold War. Abnormal droughts and flooding affected crops in Russia and China, which could’ve led to massive problems worldwide.
The ramifications of climate change have become more apparent to everyone in the 21st century. In 2021, heavy amounts of snow and rain affected the Rhine River, which flows through six countries. In February, the banks started bursting, preventing shipping for a few days. A drought caused record-low water levels by April, so ships had to lessen their load capacities.
How will rising ocean temperatures affect the supply chain of food?
Unfortunately, climate change does not seem to be getting any better. Global warming has devastating ramifications for industries worldwide. With rising ocean temperatures, one sector climate change directly impacts is the seafood industry. Catching, shipping, and selling seafood is a gigantic industry in the United States, with over $200 billion in sales yearly.
The seafood industry is especially critical in New England. Rising ocean temperatures have shifted lobster populations farther north. Lobster fishing was prevalent as far south as Delaware and Virginia, but the lobsters have migrated to Maine and may keep going.
In 1996, New York lobster fishers set a record of 9.4 million pounds, but 18 years later, the yield dropped to under 216,000 pounds, an almost 98% decrease. A similar story has happened with other New England states like Connecticut and Rhode Island, which both saw significant dips in lobster yields.
How will rising ocean temperatures affect the supply chain of seafood? Lobsters need temperatures around 68 F. Even a slight temperature difference can cause health problems for these sea creatures and cause difficulties in reproducing. Fewer lobsters mean there could be fewer jobs in the coming years. Prices will increase as supply dwindles and demand stays steady.
What are governments doing to mitigate the problem?
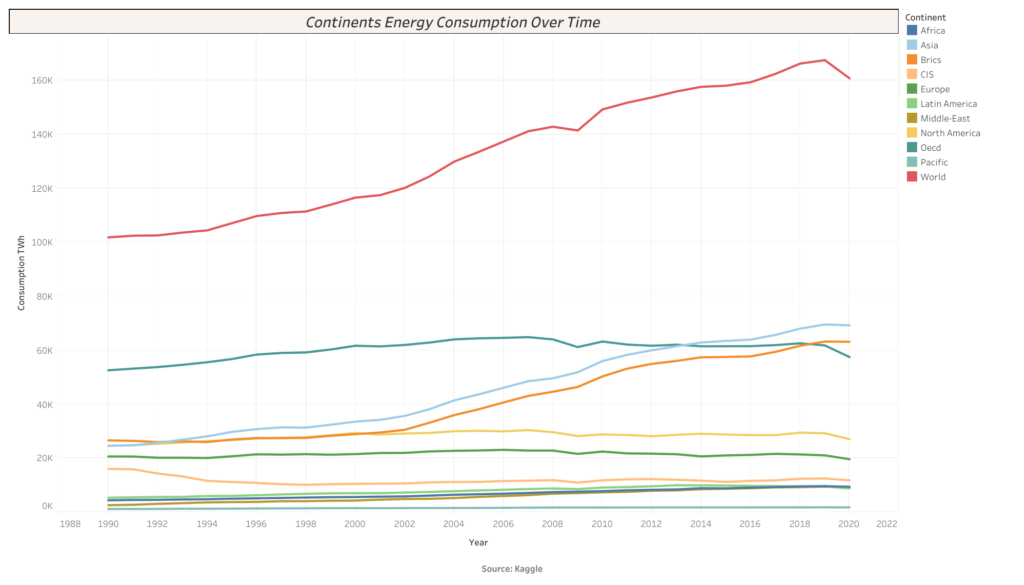
Global energy consumption has steadily increased annually over the last three decades. Countries like the United States and China consume massive amounts of power due to high demand, especially in the industrial sectors. Increased use means a large carbon footprint for each nation. Not all hope is lost, though. Many countries lean on scientists and the private sector to push for cleaner energy sources.
In September 2021, El Salvador recognized bitcoin as a legal currency, making it the first country to do so. Bitcoin can be an environmental hazard, so El Salvador has started to use geothermal energy from volcanoes to create clean and inexpensive energy for the currency. This strategy could influence larger nations to do the same if it works.
Climate change and transportation
Some countries are highly dependent on fossil fuels but are transitioning to cleaner energy sources. What does this mean for regular consumers? They’ll soon see companies phase out fossil fuels in favor of renewable power, whether by the business’s choice or government regulations.
An excellent example is the automotive industry. Manufacturers are switching to electric vehicles (EVs), even for their most popular cars.
Automakers like Chevrolet and Dodge are discontinuing the gas-powered versions of the Corvette and Charger in favor of electric models starting in late 2023 into 2024. Ford, one of the primary competitors of Dodge and Chevy, has been hesitant with electric vehicles but recently announced a $50 billion investment in EVs.
Manufacturers are switching to EVs for multiple reasons. One is the influence of investors who see an opportunity for lower production costs and higher profits. How will rising ocean temperatures affect the supply chain for cars? These companies hope EVs will ease the international supply chain because they’re easier to maintain and are better for the environment.
How will rising ocean temperatures affect future supply chains?
The devastating effects of climate change are here, and experts say the world has seen them for 50 years or more. Efforts to make a better Earth are noble and underway, but they may be too late.
Unless governments and companies change rapidly in the next few years, the UN has said that much of what global warming has done is irreversible. There is a small window of opportunity to spare people from the worst.
Every region in the United States will see devastating effects on people, businesses, and the supply chain. In the Southeast, extreme heat will negatively affect agriculture and energy, two significant parts of the region’s economy and supply chain.
High temperatures and drought are already problems in the Southwest. Agriculture will decline in the future, and the extreme heat will cause health issues in many cities. Droughts and dry air will lead to more severe wildfires. Water supplies will decrease, and flooding and erosion will be problematic for people living in coastal areas.
Focus on collective action
How has climate change affected day-to-day life? Depending on where people live, the effects could be challenging to see. However, if people start working collectively, they can fight back against climate change while there’s still time to make a difference.
Author Bio
Oscar Collins is the editor-in-chief at Modded, where he writes about sustainability, green living, and similar topics. Follow him on Twitter @TModded for frequent updates!













No Comments